Updated 2 days ago
Best Fitness Trackers for Sleep Tracking 2026: Comprehensive Guide to Accurate Sleep Analysis
youhong
Last Updated: February 5, 2026 | Expert Analysis of Sleep Monitoring Technology
Sleep tracking has evolved from simple motion detection into sophisticated biosensor analysis capable of rivaling clinical sleep studies. As research continues to reveal the profound connection between sleep quality and overall health—affecting everything from immune function to cognitive performance—the demand for accurate, actionable sleep data has never been higher.
In 2026, fitness trackers leverage advanced optical sensors, AI algorithms, and multi-modal biosignals to decode your sleep with unprecedented precision. Unlike the accelerometer-only devices of the past decade, today's best sleep trackers combine heart rate variability analysis, skin temperature monitoring, blood oxygen measurement, and respiratory pattern detection to provide comprehensive sleep architecture insights.
This guide examines the current state of sleep tracking technology, explains what metrics actually matter, compares different device categories (bands, watches, rings), and helps you identify the right sleep tracker for your specific needs—whether you're optimizing athletic recovery, managing a sleep disorder, or simply seeking better rest.
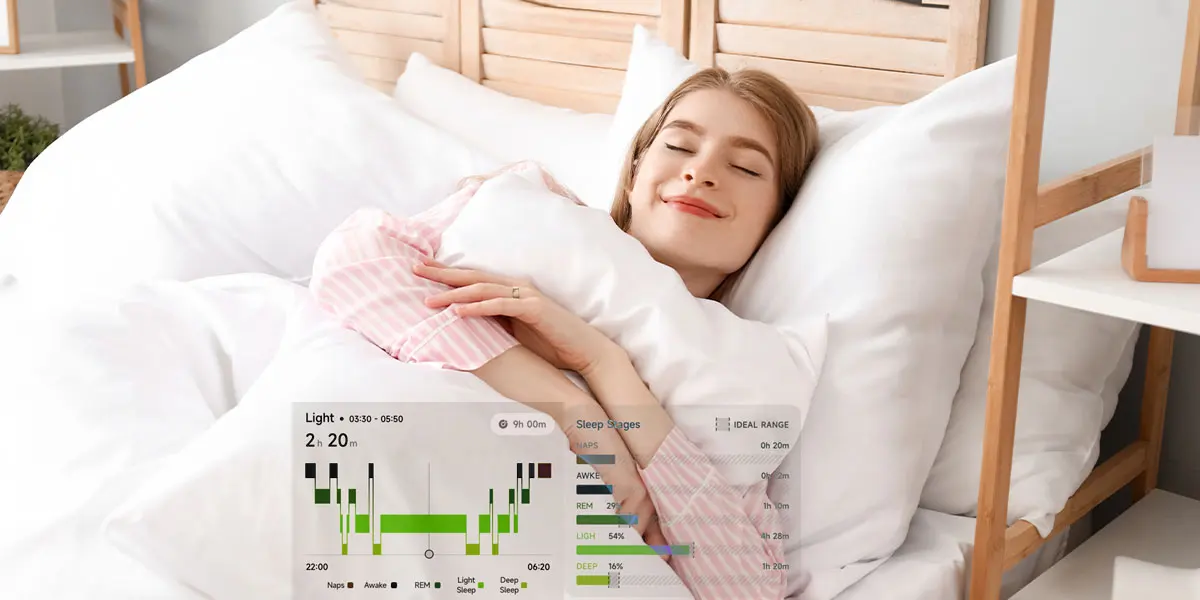

Table of Contents
- Understanding Sleep Tracking Technology
- Key Sleep Metrics Explained
- Sleep Tracker Categories Comparison
- Clinical Accuracy: What the Research Shows
- Essential Features for Effective Sleep Tracking
- Sleep Tracker Selection Guide
- Featured Solutions: Advanced Sleep Monitoring
- Improving Sleep with Tracker Data
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Sleep Tracking Technology
How Modern Sleep Trackers Work
Current-generation sleep trackers employ multiple sensing technologies working in concert:
1. Motion Sensors (Accelerometer + Gyroscope)
Technology:
Three-axis accelerometers measure movement in X, Y, and Z directions, while gyroscopes detect rotational movement.
Sleep Application:
- Detects major body position changes (rolling over)
- Identifies micro-movements indicating sleep stages
- Distinguishes sleep from wake (extended stillness vs. activity)
Accuracy:
Motion alone provides ~75-85% sleep/wake detection accuracy compared to clinical polysomnography (PSG). However, it struggles with sleep stage differentiation.
2. Optical Heart Rate Monitoring (PPG)
Technology:
Photoplethysmography uses LED lights (typically green) to detect blood volume changes in capillaries beneath the skin.
- Resting heart rate (RHR) decreases during sleep
- Heart rate patterns differ across sleep stages:
- Deep sleep: Lowest and most stable heart rate
- REM sleep: More variable heart rate, approaching waking levels
- Light sleep: Moderate heart rate, some variability
Accuracy:
High-quality PPG sensors achieve 95-99% accuracy for resting heart rate measurement during sleep.
3. Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
Technology:
Precise measurement of time intervals between heartbeats (R-R intervals from PPG signal).
Sleep Application:
- High HRV during sleep: Indicates parasympathetic dominance (rest-and-digest state)
- Low HRV during sleep: Suggests stress, overtraining, or illness
- HRV patterns help distinguish sleep stages (higher during deep sleep)
Clinical Significance:
HRV is one of the strongest biomarkers for recovery status and overall autonomic nervous system health.
4. Blood Oxygen (SpO2) Monitoring
Technology:
Dual-wavelength LEDs (red 660nm + infrared 940nm) measure oxygen saturation in hemoglobin.
Sleep Application:
- Detects sleep apnea events (oxygen desaturation episodes)
- Normal sleep: 95-100% SpO2
- Sleep apnea: Repeated drops below 90%
- FDA-cleared algorithms can identify obstructive sleep apnea patterns
Accuracy:
Wrist-based SpO2: ±2-3% accuracy during sleep (adequate for screening, not medical diagnosis).
5. Skin Temperature Sensing
Technology:
Thermopile or thermistor sensors measure skin surface temperature.
Sleep Application:
- Core body temperature drops during sleep (circadian rhythm)
- Temperature fluctuations correlate with sleep stages
- Elevated temperature may indicate illness or fever
- Women's health: Temperature tracking reveals menstrual cycle phases
Accuracy:
±0.1-0.3°C precision for relative temperature trends.
6. Respiratory Rate Detection
Technology:
Derived from PPG signal modulation caused by breathing or from chest movement (accelerometer).
Sleep Application:
- Normal sleep breathing: 12-20 breaths/minute
- Respiratory rate changes across sleep stages
- Irregular patterns may indicate sleep-disordered breathing
Accuracy:
±2 breaths/minute typical accuracy during sleep.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Modern sleep trackers employ sophisticated AI algorithms to:
Pattern Recognition:
- Learn individual sleep baselines over weeks/months
- Identify personal sleep architecture patterns
- Distinguish between sleep stages with 70-85% accuracy (vs. clinical PSG)
Anomaly Detection:
- Flag unusual patterns (e.g., sudden increase in RHR, oxygen desaturation)
- Detect early signs of illness (elevated skin temperature, altered HRV)
- Identify sleep disruptions (environmental noise, stress)
Personalized Insights:
- Correlate lifestyle factors (caffeine, exercise timing, stress) with sleep quality
- Provide tailored recommendations based on trends
- Predict optimal bedtime based on historical data

Key Sleep Metrics Explained
Essential Sleep Metrics
1. Sleep Duration
What It Measures:
Total time asleep from first sleep onset to final awakening.
Optimal Range:
- Adults (18-64 years): 7-9 hours
- Older adults (65+): 7-8 hours
Why It Matters:
Chronic sleep deprivation (<7 hours consistently) is linked to increased risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, cognitive decline, and mortality.
Tracker Accuracy:
High-quality trackers measure total sleep time within ±10-20 minutes of clinical PSG.
2. Sleep Stages
What It Measures:
Distribution of time across four sleep stages.
Stage Descriptions:
Light Sleep (N1 + N2):
- Transition between wake and deeper sleep
- Easily awakened
- Comprises 45-55% of total sleep
- Facilitates memory consolidation
Deep Sleep (N3, Slow-Wave Sleep):
- Hardest to wake from
- Physical restoration, muscle repair, immune system strengthening
- Human growth hormone release
- Comprises 15-25% of total sleep (higher in younger adults)
- Critical for feeling refreshed
REM Sleep (Rapid Eye Movement):
- Vivid dreams occur
- Emotional processing and memory consolidation
- Brain highly active (similar to wakefulness)
- Comprises 20-25% of total sleep
- Increases in duration toward morning
Awake Time:
- Brief awakenings throughout night (normal)
- Should total <5% of time in bed
- Excessive awakenings indicate poor sleep quality
Tracker Accuracy:
Best trackers achieve 70-85% sleep stage classification accuracy compared to PSG. This is adequate for trend tracking but not clinical diagnosis.
3. Sleep Efficiency
What It Measures:
(Total Sleep Time / Time in Bed) × 100%
Example:
- Time in bed: 8 hours (480 minutes)
- Total sleep time: 7 hours (420 minutes)
- Sleep efficiency: (420/480) × 100% = 87.5%
Optimal Range:
- Healthy adults: 85-95%
- <85%: May indicate sleep disorder or poor sleep hygiene
95%: May suggest insufficient sleep opportunity (going to bed too late)
Why It Matters:
Sleep efficiency is often more important than duration—quality over quantity.
4. Sleep Onset Latency
What It Measures:
Time from getting into bed to falling asleep.
Optimal Range:
- Healthy: 10-20 minutes
- <5 minutes: May indicate sleep deprivation
30 minutes: May indicate insomnia or poor sleep hygiene
5. Sleep Debt
What It Measures:
Cumulative difference between sleep need and actual sleep obtained over recent days (typically 7-14 day period).
Example:
- Need: 8 hours/night
- Actual average: 6.5 hours/night
- Daily deficit: 1.5 hours
- Weekly debt: 10.5 hours
Why It Matters:
Sleep debt accumulates and impairs cognitive performance, mood, and health—even if you don't feel subjectively sleepy.
6. Recovery Score / Sleep Score
What It Measures:
Composite metric combining multiple factors:
- Sleep duration
- Sleep quality (stage distribution)
- Resting heart rate
- Heart rate variability
- Respiratory rate
- Blood oxygen levels
- Restlessness
Typical Scale:
0-100, where 85+ = excellent recovery, 70-84 = good, <70 = poor
Why It Matters:
Simplifies complex data into actionable daily guidance: "Ready for intense training" vs. "Prioritize rest today."

Sleep Tracker Categories Comparison
Fitness Bands vs. Smartwatches vs. Smart Rings
| Feature | Fitness Bands | Smartwatches | Smart Rings |
| Form Factor | Wrist strap, small display | Watch-style, large display | Finger ring, no display |
| Weight | 25-35g | 40-80g | 3-7g ⭐ |
| Sleep Comfort | Good (94% wear overnight) | Fair (67% wear overnight) | Excellent (98% wear overnight) ⭐ |
| Battery Life | 7-21 days ⭐ | 18hrs-7 days | 4-14 days |
| Sleep Stage Accuracy | 75-88% | 73-86% | 82-95% ⭐ |
| Temperature Monitoring | Rare (premium only) | Rare (select models) | Common ⭐ |
| Price Range | 50-200 | 200-1,200 | 200-500 |
| Best For | All-around tracking | Smartphone integration + fitness | Sleep specialization |
Key Insights:
Smart Rings Lead Sleep Tracking:
- Superior comfort = higher overnight compliance
- Finger placement provides excellent temperature and HRV signals
- Less affected by movement artifacts during sleep
Fitness Bands Best Value:
- Good sleep tracking + activity monitoring
- Long battery life means no charging gaps
- Affordable for most budgets
Smartwatches Most Versatile:
- Sleep tracking + comprehensive smartwatch features
- Larger displays for detailed overnight data review
- Battery life remains primary limitation

Clinical Accuracy: What the Research Shows
Independent Validation Studies (2024-2026)
Multi-Device Comparison Study (2024):
A prospective multicenter study published in medical journals evaluated 11 consumer sleep trackers against clinical polysomnography:
Sleep/Wake Detection Accuracy:
- Best performers: 85-90% accuracy
- Average performers: 75-85% accuracy
- Weak performers: 65-75% accuracy
Sleep Stage Classification (Macro F1 Score):
- Best performers: 0.65-0.69 (approaching clinical utility)
- Average performers: 0.45-0.60
- Weak performers: 0.26-0.40
Performance by Stage:
- Wake detection: Most accurate (85-95%)
- REM sleep: Moderate accuracy (70-85%)
- Deep sleep: Variable (60-85%, device-dependent)
- Light sleep: Least accurate (often confused with other stages)
Key Finding:
Even the best consumer sleep trackers achieve ~80% stage classification accuracy compared to PSG. While insufficient for clinical diagnosis, this provides actionable insights for personal optimization.
Accuracy Factors
What Affects Sleep Tracking Accuracy:
Device-Related:
✅ Sensor quality (5-LED PPG arrays outperform 2-LED)
✅ Algorithm sophistication (AI-trained models on large datasets)
✅ Firmware updates (continuous algorithm improvements)
User-Related:
✅ Proper fit (snug but not tight, consistent placement)
✅ Skin tone (darker skin may reduce PPG accuracy slightly)
✅ Wrist hair density (can interfere with optical sensors)
✅ Tattoos over sensor location (blocks light transmission)
Environmental:
✅ Room temperature (extreme cold/heat affects skin blood flow)
✅ Alcohol consumption (alters sleep architecture and HRV)
✅ Medication (some drugs affect heart rate, sleep stages)
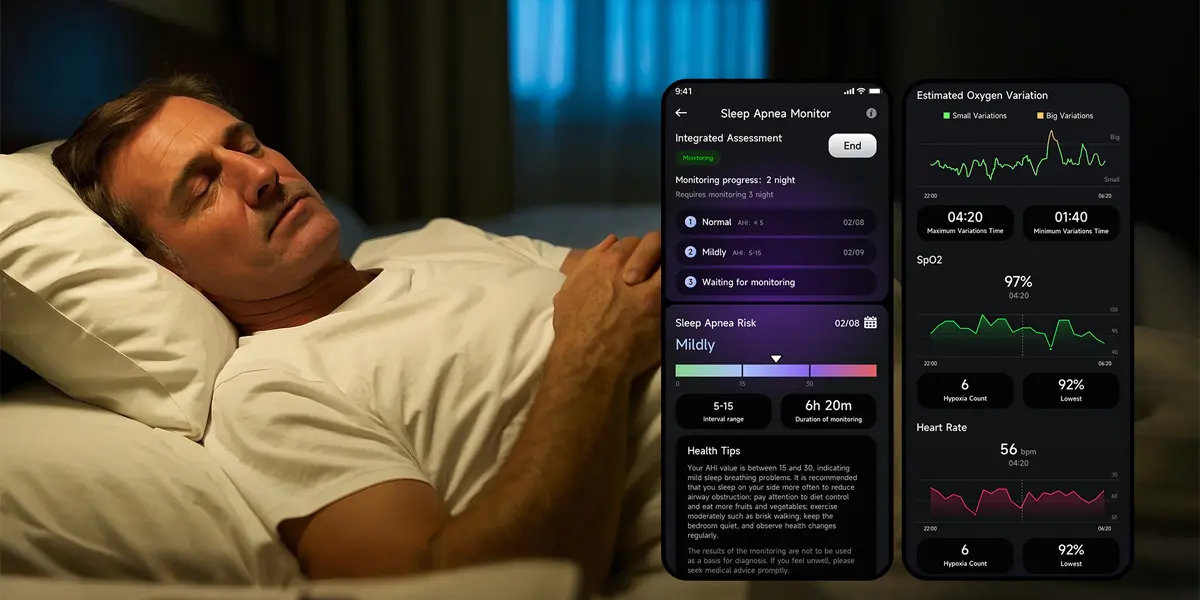
Essential Features for Effective Sleep Tracking
Must-Have Features
1. Automatic Sleep Detection
✅ Tracker automatically starts/stops sleep recording (no manual activation)
✅ Detects naps (daytime sleep episodes)
✅ Accuracy: Should detect sleep onset within 15 minutes
2. Multi-Night Trend Analysis
✅ Minimum 30-60 days of historical data storage
✅ Weekly and monthly trend visualization
✅ Comparison to personal baselines and population averages
3. Sleep Stage Breakdown
✅ Light, deep, REM, and wake time percentages
✅ Sleep stage timeline (visual representation of overnight progression)
✅ Stage duration trends over time
4. Smart Wake-Up / Sleep Alarm
✅ Wakes you during light sleep within target window (e.g., 7:00-7:30 AM)
✅ Reduces grogginess from deep sleep awakening
✅ Gentle vibration or sound escalation
5. Sleep Score / Recovery Metric
✅ Simplified daily score (0-100 scale typical)
✅ Clear explanation of score components
✅ Actionable guidance ("Prioritize recovery today")
Advanced Features (Differentiators)
6. SpO2 Monitoring for Sleep Apnea Screening
✅ Continuous or periodic oxygen saturation measurement
✅ Oxygen desaturation event detection
✅ Sleep apnea risk assessment (FDA-cleared algorithms on select devices)
Why It Matters:
An estimated 22 million Americans have sleep apnea; most are undiagnosed. SpO2 screening can prompt medical evaluation.
7. Temperature Tracking
✅ Skin temperature trends across night
✅ Deviation alerts (fever detection)
✅ Women's health: Ovulation and cycle phase correlation
8. Respiratory Rate Monitoring
✅ Breathing patterns throughout sleep
✅ Average breaths per minute
✅ Irregularity detection
9. HRV Analysis
✅ Overnight heart rate variability measurement
✅ Trend comparison (rising HRV = improving recovery)
✅ Stress and readiness correlation
10. Sleep Debt Calculation
✅ Cumulative sleep deficit tracking (7-14 day window)
✅ Recovery recommendations
✅ Long-term trend visualization
11. Environmental Factor Correlation
✅ Log caffeine, alcohol, exercise timing
✅ Automatic correlation with sleep quality
✅ Personalized insights ("Caffeine after 3 PM reduces deep sleep by 18%")

Sleep Tracker Selection Guide
Choosing Based on Your Goals
Goal 1: Athletic Performance & Recovery Optimization
Best Device Type: Fitness band or sport-focused smartwatch
Critical Features:
- HRV tracking (primary recovery indicator)
- Sleep efficiency and deep sleep percentage
- Training load integration
- Recovery score guiding workout intensity
Recommendations:
- Look for devices emphasizing recovery analytics
- Prioritize HRV accuracy over stage classification perfection
- Choose extended battery life (no gaps in overnight tracking)
Goal 2: Sleep Disorder Screening (Apnea, Insomnia)
Best Device Type: Device with SpO2 monitoring and medical-grade features
Critical Features:
- Continuous SpO2 measurement during sleep
- Oxygen desaturation event detection
- Sleep onset latency and efficiency tracking
- Data export for healthcare providers
Important Note:
Consumer trackers are screening tools, not diagnostic devices. Abnormal patterns should prompt medical consultation and formal sleep study if indicated.
Goal 3: General Wellness & Sleep Optimization
Best Device Type: Fitness band offering good value and comprehensive tracking
Critical Features:
- Sleep stage breakdown (light, deep, REM)
- Sleep score simplifying data interpretation
- Long battery life (minimal user maintenance)
- Actionable sleep hygiene recommendations
Recommendations:
- Prioritize user-friendly apps with clear visualizations
- Balance sleep tracking with daytime activity features
- Consider budget-friendly options ($80-150)
Goal 4: Women's Health & Cycle Tracking
Best Device Type: Smart ring or fitness band with temperature monitoring
Critical Features:
- Precise skin temperature measurement (±0.1-0.3°C)
- Automatic cycle phase detection
- Fertility window prediction
- Sleep quality correlation with hormonal phases
Why Temperature Matters:
Basal body temperature rises 0.3-0.5°C after ovulation, enabling cycle tracking. Sleep quality often decreases during late luteal/menstrual phases.
Goal 5: Stress Management & Mental Health
Best Device Type: Device emphasizing HRV and stress metrics
Critical Features:
- Daily HRV measurement and trends
- Stress score calculation
- Mindfulness/meditation integration
- Sleep-stress correlation analysis
Why It Matters:
Poor sleep elevates stress; chronic stress disrupts sleep. Breaking this cycle requires monitoring both.
Budget Considerations
Budget Tier (50-100):
- Basic sleep tracking (motion + HR)
- Sleep duration and simple stage estimation
- Good battery life (7-14 days)
- Limited advanced features
- Best For: Sleep awareness beginners
Mid-Range Tier (100-250):
- Advanced sleep stage analysis
- HRV and recovery metrics
- SpO2 monitoring (select models)
- Comprehensive app with trends
- Best For: Most users seeking actionable insights
Premium Tier (250-500):
- Medical-grade sensor accuracy
- Temperature monitoring
- Advanced AI insights
- Long-term trend analysis
- FDA-cleared features (select models)
- Best For: Serious athletes, health optimization enthusiasts
Featured Solutions: Advanced Sleep Monitoring
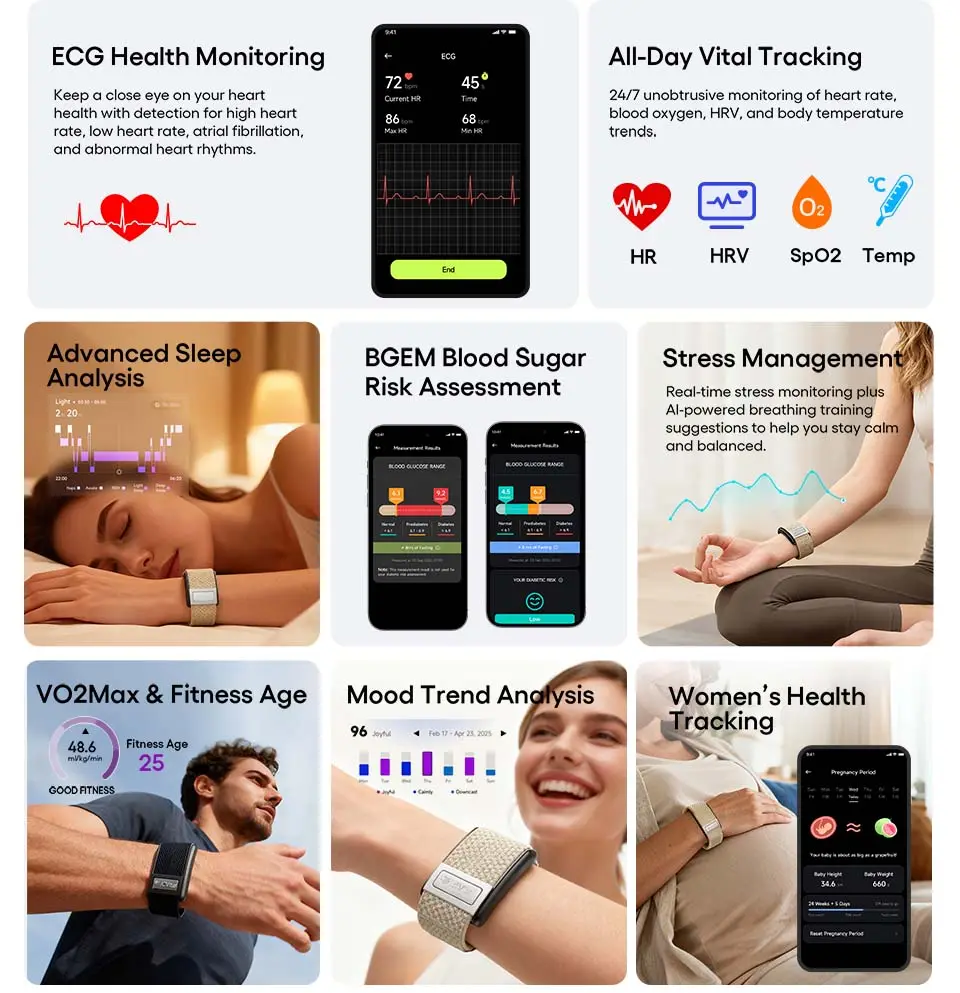
While the market offers numerous sleep tracking options across all price ranges, certain specialized fitness bands stand out for their comprehensive approach to sleep analysis. Below are two examples that represent current trends in AI-powered sleep monitoring and medical-grade health tracking.
AI-Powered Sleep Analysis Bands
Modern fitness bands increasingly incorporate artificial intelligence to transform raw sensor data into actionable sleep insights. These devices typically offer:
Comprehensive Sleep Architecture Analysis:
- Automatic sleep detection with no manual activation
- Detailed breakdown of sleep stages (light, deep, REM, wake)
- Sleep cycle visualization showing the progression through 4-6 cycles per night
- Sleep efficiency calculations comparing actual sleep time to time in bed
AI-Driven Recovery Systems:
Advanced machine learning algorithms analyze multiple data streams simultaneously:
- Sleep duration relative to individual needs
- Sleep quality metrics including stage distribution
- Overnight heart rate variability patterns
- Resting heart rate trends
- Movement and restlessness indicators
These systems generate daily recovery scores (typically 0-100 scale) with personalized recommendations for activity levels, helping users understand whether they're ready for intense training or should prioritize rest.
Example: JCVital V5
The V5 Smart AI Health Band represents this category, offering deep sleep structure analysis with AI-powered recovery insights and evidence-based sleep improvement guidance. Its multi-sensor array combines PPG heart rate monitoring with accelerometer data for comprehensive 24/7 tracking.
Medical-Grade ECG-Enhanced Sleep Monitoring
At the premium end of the fitness band market, devices with clinical-grade sensors provide hospital-level accuracy for health monitoring alongside sophisticated sleep analytics.
Comprehensive Automated Sleep Metrics:
Sleep Time Analysis:
- Total time in bed vs. total sleep time
- Sleep onset latency (time required to fall asleep)
- Number and timing of awakenings throughout the night
- Final awakening time
Detailed Sleep Quality Assessment:
- Deep sleep duration and percentage (physical restoration phase)
- Light sleep duration and percentage (transitional stages)
- REM sleep duration and percentage (cognitive processing phase)
- Wake time distribution and frequency
Advanced Sleep Analytics:
- Sleep efficiency ratios with trend analysis over 7/30/90-day periods
- Sleep debt tracking showing cumulative deficits
- Sleep recovery index incorporating duration, quality, HRV, and heart rate normalization
- Personalized sleep pattern identification
- Environmental and lifestyle factor correlation
- Long-term sleep health trend visualization
Example: JCVital V8
The JCVital V8 ECG Smart Band exemplifies this category with medical-grade sensors delivering clinical-grade accuracy. Beyond comprehensive sleep tracking, it offers ECG heart rhythm monitoring, continuous HRV tracking, blood oxygen measurement, and stress assessment—all with no subscription fees for full feature access.
Key Considerations When Choosing Advanced Sleep Trackers
Sensor Quality Matters:
Medical-grade sensors provide more reliable data, particularly for metrics like HRV and SpO2 that inform recovery and health status.
AI vs. Basic Algorithms:
Devices employing machine learning algorithms trained on large datasets can identify personal patterns and provide more accurate sleep stage classification than simple rule-based systems.
Data Ownership and Privacy:
Look for devices that encrypt health data, allow user-controlled sharing, and don't sell information to third parties.
Subscription Model:
Some premium features require ongoing subscriptions. Devices offering complete functionality with one-time purchase provide better long-term value.
Battery Life:
Extended battery life (7+ days) ensures continuous data collection without gaps from charging cycles.
Improving Sleep with Tracker Data
Actionable Insights from Sleep Data
1. Identifying Sleep Debt Patterns
Data to Monitor:
- Weekly average sleep duration
- Night-to-night variability
- Cumulative sleep debt trends
Action Steps:
- If chronic debt accumulates: Gradually extend sleep opportunity by 15-30 minutes per night
- Prioritize consistency: Go to bed and wake at same times (even weekends)
- Weekend recovery: Sleeping 1-2 hours extra can partially repay debt, but consistency is better
2. Optimizing Deep Sleep
Data to Monitor:
- Deep sleep percentage (target: 15-25% of total sleep)
- Deep sleep duration trends
Factors Improving Deep Sleep:
✅ Regular exercise (but not within 3 hours of bedtime)
✅ Cool bedroom temperature (65-68°F / 18-20°C optimal)
✅ Avoiding alcohol (suppresses deep sleep)
✅ Consistent sleep schedule (trains circadian rhythm)
✅ Morning light exposure (strengthens sleep-wake cycle)
3. Enhancing REM Sleep
Data to Monitor:
- REM percentage (target: 20-25% of total sleep)
- REM timing (normally increases toward morning)
Factors Improving REM:
✅ Adequate total sleep (REM requires sufficient opportunity)
✅ Avoid late-night screen time (blue light delays REM onset)
✅ Manage stress (chronic stress suppresses REM)
✅ Avoid alcohol before bed (disrupts REM cycles)
4. Reducing Sleep Fragmentation
Data to Monitor:
- Number of awakenings per night
- Restlessness/movement frequency
- Wake time percentage
Common Causes & Solutions:
- Frequent bathroom trips: Limit fluids 2-3 hours before bed
- Temperature discomfort: Adjust room temp, bedding layers
- Sleep apnea: Consult physician if SpO2 drops detected
- Stress/anxiety: Practice relaxation techniques, consider CBT-I (cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia)
5. Leveraging HRV for Recovery
Data to Monitor:
- Overnight HRV trends
- HRV comparison to personal baseline
Interpreting HRV:
- Rising HRV: Good recovery, ready for training
- Declining HRV: Stress, overtraining, or illness—prioritize rest
- Consistently low HRV: Consider lifestyle modifications (reduce stress, improve sleep, moderate training)
Evidence-Based Sleep Hygiene Practices
Environmental Optimization:
- Temperature: 65-68°F (18-20°C) for optimal sleep
- Light: Complete darkness or eye mask (blocks melatonin suppression)
- Noise: White noise machines or earplugs for consistent sound environment
- Mattress/Pillows: Replace every 7-10 years; proper spinal alignment
Behavioral Strategies:
- Consistent schedule: Same bedtime/wake time daily (±30 minutes)
- Wind-down routine: 30-60 minutes of relaxing activities before bed
- Caffeine cutoff: No caffeine after 2 PM (6-8 hour half-life)
- Alcohol moderation: While sedating initially, alcohol fragments sleep and suppresses REM
- Exercise timing: Morning or afternoon preferred; finish vigorous exercise 3+ hours before bed
- Screen time: Avoid blue light 1-2 hours before bed or use blue-blocking glasses
Dietary Considerations:
- Light dinner: Heavy meals within 3 hours of bed disrupt sleep
- Hydration balance: Adequate fluids during day, minimal 2 hours before bed
- Sleep-promoting nutrients: Magnesium, tryptophan, complex carbohydrates
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How accurate are fitness tracker sleep stages compared to clinical sleep studies?
A: Current best-performing consumer sleep trackers achieve approximately 70-85% sleep stage classification accuracy compared to polysomnography (PSG), the clinical gold standard.
Detailed Breakdown:
Sleep/Wake Detection:
- High-quality trackers: 85-95% accuracy
- This is the most reliable metric—trackers excel at determining if you're asleep vs. awake
Sleep Stage Classification:
| Stage | Tracker Accuracy | Clinical Significance |
| Wake | 85-95% | Excellent reliability |
| REM Sleep | 70-85% | Moderate reliability |
| Deep Sleep | 60-85% | Variable by device |
| Light Sleep | 60-75% | Often confused with other stages |
Why the Gap Exists:
Clinical PSG Uses:
- Electroencephalography (EEG) - brain wave patterns (definitive for stages)
- Electrooculography (EOG) - eye movements (essential for REM detection)
- Electromyography (EMG) - muscle activity
- These directly measure brain and body states defining sleep stages
Consumer Trackers Use:
- Motion sensors (accelerometer/gyroscope)
- Heart rate and HRV (indirect markers)
- Respiratory rate
- Blood oxygen levels (SpO2)
- Skin temperature
Bottom Line: Trackers infer sleep stages from physiological proxies rather than measuring brain activity directly. This provides useful trends and patterns but not clinical-grade diagnosis.
Practical Implication:
Sleep trackers are excellent for:
✅ Tracking sleep duration and consistency
✅ Identifying sleep efficiency problems
✅ Monitoring trends over weeks/months
✅ Correlating lifestyle changes with sleep quality
Sleep trackers are NOT suitable for:
❌ Diagnosing sleep disorders (requires physician and PSG)
❌ Precise stage classification for medical decisions
❌ Detecting complex sleep pathologies
Research Evidence:
A 2024 multicenter validation study testing 11 consumer sleep trackers found macro F1 scores (stage classification accuracy) ranging from 0.26 to 0.69, with best performers approaching but not matching clinical utility thresholds.
Q: Which type of device is best for sleep tracking: band, watch, or ring?
A: Smart rings generally provide the most accurate sleep tracking, though each form factor has distinct advantages:
Smart Rings: Best Sleep Accuracy ⭐
Advantages:
✅ Superior comfort: 98% overnight wear compliance (vs. 67% for watches)
✅ Finger placement benefits: Digital arteries provide strong, consistent signals for temperature and HRV
✅ Minimal movement: Fingers move less than wrists during sleep, reducing artifacts
✅ Temperature sensing: Common feature in rings, rare in bands/watches
✅ Sleep stage accuracy: 82-95% in clinical studies (best category)
Disadvantages:
❌ No display (must check phone for data)
❌ Higher cost (200-500 typical)
❌ Limited activity tracking during workouts
❌ Fixed sizing (can't adjust like watch strap)
Best For: Sleep optimization focus, women's health tracking, recovery monitoring
Fitness Bands: Best Value ⭐
Advantages:
✅ Long battery life: 7-21 days (no charging gaps disrupting data)
✅ Good sleep accuracy: 75-88% stage classification
✅ Affordable: 50-200 range
✅ Comprehensive: Sleep + daytime activity in one device
✅ Comfortable: 94% overnight wear compliance
Disadvantages:
❌ Wrist placement less ideal than finger for some metrics
❌ Occasional temperature sensing (premium models only)
Best For: All-around health tracking, budget-conscious users, athletes needing both sleep and workout data
Smartwatches: Most Versatile
Advantages:
✅ Large display: Easy overnight data review on wrist
✅ Full smartwatch features: Sleep tracking + notifications, apps, payments
✅ Good accuracy: 73-86% stage classification
Disadvantages:
❌ Poor battery life: Most require daily charging (data gaps)
❌ Bulky for sleep: Only 67% wear overnight consistently
❌ Expensive: 200-1,200 range
Best For: Users wanting all-in-one device, willing to charge nightly, prioritizing smartwatch features over sleep specialization
Comparison Summary:
| Priority | Best Device Type |
| Maximum sleep accuracy | Smart Ring |
| Best value | Fitness Band |
| All-around features | Smartwatch |
| Longest battery life | Fitness Band |
| Overnight comfort | Smart Ring |
| Budget under $150 | Fitness Band |
Recommendation: If sleep is your primary concern and budget allows (
Q: Can sleep trackers detect sleep apnea?
A: Some sleep trackers can screen for sleep apnea risk through blood oxygen monitoring, but they cannot diagnose the condition.
What Sleep Trackers Can Do:
SpO2-Enabled Devices:
Measure oxygen saturation continuously or periodically throughout sleep.
Sleep Apnea Indicators:
- Oxygen desaturation events: Drops below 90% SpO2
- Desaturation frequency: Multiple events per hour
- Heart rate irregularities: Spikes following apnea episodes
- Respiratory rate abnormalities: Pauses or irregular breathing patterns
FDA-Cleared Features (Select Devices):
Some smartwatches have received FDA clearance for sleep apnea detection algorithms. These analyze:
- SpO2 patterns
- Heart rate variability
- Respiratory effort estimation
- Movement patterns
Examples: Certain premium smartwatches received FDA approval in 2024-2025 for sleep apnea risk notification.
What Sleep Trackers CANNOT Do:
❌ Definitive diagnosis: Only clinical polysomnography (PSG) or home sleep apnea tests (HSAT) can diagnose
❌ Severity classification: Cannot determine if apnea is mild, moderate, or severe
❌ Type differentiation: Cannot distinguish obstructive vs. central vs. complex sleep apnea
❌ Treatment guidance: Cannot prescribe CPAP pressure or other therapies
Appropriate Use:
Screening Tool:
If your tracker consistently shows:
- SpO2 drops below 90% multiple times nightly
- Oxygen desaturation index (ODI) >5 events/hour
- Irregular breathing patterns
Action: Consult a physician and request formal sleep study.
Not for Diagnosis:
Do NOT use tracker data alone to:
- Self-diagnose sleep apnea
- Initiate treatment without medical consultation
- Adjust CPAP settings
- Determine treatment efficacy
Q: How long should I wear a sleep tracker before seeing meaningful patterns?
A: Minimum 2 weeks for initial patterns; 4-8 weeks for reliable personal baselines.
Timeline for Insights:
Week 1-2: Initial Data Collection
- Tracker learns your typical sleep/wake times
- Establishes baseline resting heart rate
- Identifies average sleep duration
- Action: Wear consistently; avoid changing sleep habits yet
Week 3-4: Pattern Emergence
- Week-to-week comparisons become possible
- Sleep debt trends visible
- Correlation with daily activities begins
- Action: Start logging lifestyle factors (exercise, caffeine, alcohol)
Week 5-8: Reliable Baselines
- Personal sleep architecture norms established
- HRV baseline stabilizes
- Meaningful anomaly detection possible
- Action: Begin implementing evidence-based changes; track impact
Month 3+: Long-Term Optimization
- Seasonal variations visible
- Training/recovery patterns clear
- Lifestyle intervention effectiveness quantified
- Action: Fine-tune sleep optimization strategies
Best Practice:
Wear your tracker continuously for at least 30 consecutive nights before drawing major conclusions about your sleep health.
Q: Do I need to manually start sleep tracking, or is it automatic?
A: Modern sleep trackers (2024+) use automatic sleep detection, requiring no manual activation.
How Automatic Detection Works:
Detection Triggers:
- Extended period of stillness (typically 30-60 minutes)
- Heart rate drops to resting levels
- Consistent horizontal body position
- Time of day (algorithms expect sleep during typical hours)
Accuracy:
- Sleep onset detection: Within ±10-15 minutes for quality trackers
- Wake detection: Within ±5-10 minutes
- Nap detection: 20+ minute episodes during daytime
Manual Override:
Most trackers also allow:
- Manual sleep mode activation (if you want to ensure tracking)
- Editing sleep times after the fact (correcting missed detection)
- Nap logging (if automatic nap detection missed short episodes)
Best Practice:
Trust automatic detection for routine use. Only use manual mode for:
- Unusual sleep schedules (shift work, jet lag)
- Very short naps (under 20 minutes)
- When you notice consistent detection errors
Q: Will wearing a fitness tracker to bed be uncomfortable?
A: Comfort varies significantly by device type and individual preference:
Comfort Rankings (User Surveys):
Smart Rings: 98% find comfortable for overnight wear
- Minimal weight (3-7g)
- No protruding components
- Forget you're wearing it after adjustment period (2-3 nights)
Fitness Bands: 94% find comfortable for overnight wear
- Lightweight (25-35g)
- Low profile design
- Soft silicone straps reduce irritation
- May require loosening slightly from daytime fit
Smartwatches: 67% find comfortable for overnight wear
- Heavier (40-80g)
- Bulky case can catch on bedding
- Screen protrudes from wrist
- Many users remove for sleep despite sleep tracking capability
Comfort Tips:
Proper Fit:
- Snug enough for sensor contact, loose enough to avoid pressure marks
- Position device 1-2 finger widths above wrist bone
- Loosen 1 notch at night vs. daytime wear
Band Material:
- Silicone: Flexible, hypoallergenic, easy to clean
- Fabric: Breathable but may retain moisture
- Metal: Avoid for sleep (cold, rigid, catches on bedding)
Adjustment Period:
Give yourself 5-7 nights to adapt. Most initial discomfort resolves as you unconsciously adjust sleeping positions.
Q: Can alcohol or medication affect my sleep tracking data?
A: Yes—alcohol, medications, and various substances significantly alter both actual sleep architecture and tracker readings.
Alcohol Effects:
On Actual Sleep:
- Suppresses REM sleep (especially first half of night)
- Increases deep sleep initially (first 2-3 hours)
- Causes sleep fragmentation in second half of night
- Reduces overall sleep quality despite possible increased total time
On Tracker Readings:
- Elevated heart rate (alcohol metabolism increases HR by 5-15 bpm)
- Reduced HRV (sympathetic nervous system activation)
- Increased movement/restlessness (more awakenings)
- May show less REM sleep (accurate—alcohol suppresses REM)
Typical Pattern: Tracker shows "poor recovery" after alcohol consumption—this is accurate.
Common Medication Effects:
Stimulants (ADHD medications, caffeine):
- Increased sleep onset latency
- Reduced deep sleep
- Elevated heart rate
- Lower HRV
Sedatives/Sleep Aids (benzodiazepines, Z-drugs):
- Altered sleep architecture (may not show as "normal" stages)
- Reduced REM sleep
- Tracker may misclassify sedated state vs. natural sleep
Antidepressants (SSRIs, SNRIs):
- Some suppress REM sleep
- May increase periodic limb movements
- Variable effects on sleep stages
Beta Blockers:
- Lower heart rate (may affect tracker's stage classification algorithms)
- Can reduce REM sleep
- Vivid dreams/nightmares common
Antihistamines (Benadryl, etc.):
- Increase drowsiness but reduce sleep quality
- Suppress REM sleep
- May show as fragmented light sleep
Important Considerations:
Tracker Accuracy:
Some medications alter the physiological signals trackers use for stage classification, potentially reducing accuracy. The tracker's readings may not reflect true sleep architecture.
Clinical Decisions:
Never adjust prescribed medications based solely on tracker data. Discuss sleep concerns with your healthcare provider.
Baseline Establishment:
If you take medications regularly, your personal baseline will reflect their effects. Focus on relative changes rather than comparing to population norms.
Q: Should I be concerned if my deep sleep percentage is low?
A: Low deep sleep deserves attention but requires context—age, lifestyle, and measurement accuracy all matter.
Normal Deep Sleep Ranges:
| Age Group | Typical Deep Sleep % | Deep Sleep Duration (8hr sleep) |
| 18-25 | 20-25% | 96-120 minutes |
| 26-40 | 15-20% | 72-96 minutes |
| 41-60 | 10-15% | 48-72 minutes |
| 60+ | 5-10% | 24-48 minutes |
Key Insight: Deep sleep naturally declines with age. A 50-year-old with 12% deep sleep is normal; a 25-year-old with the same percentage warrants investigation.
When to Be Concerned:
Consistent Low Deep Sleep (<10% under age 40):
Possible Causes:
- Sleep apnea or breathing disorders
- Chronic stress/anxiety
- Alcohol consumption
- Sleep environment issues (temperature, noise, light)
- Overtraining (athletes)
- Medication side effects
- Underlying health conditions
Action Steps:
- Optimize sleep environment: Cool (65-68°F), dark, quiet
- Review lifestyle factors: Eliminate alcohol, manage stress, adjust exercise timing
- Track trends: Monitor for 4-6 weeks after changes
- Medical consultation: If low deep sleep persists despite optimization, discuss with physician
Important Caveats:
Tracker Accuracy Limitations:
Consumer sleep trackers are least accurate at classifying deep sleep (60-85% accuracy). Your actual deep sleep may differ from tracker readings.
Night-to-Night Variability:
Deep sleep percentages naturally fluctuate ±5% night-to-night. Focus on weekly averages, not single nights.
Total Sleep Matters More:
If you're sleeping 6 hours with 15% deep sleep (54 minutes), extending to 8 hours may yield 12% deep sleep (58 minutes)—a net improvement despite lower percentage.
Subjective Quality:
How you feel upon waking and throughout the day matters more than any single metric. If you feel refreshed with 10% deep sleep, your sleep is working for you.
Boosting Deep Sleep:
Evidence-Based Strategies:
✅ Regular aerobic exercise (but finish 3+ hours before bed)
✅ Consistent sleep schedule (same bedtime/wake time daily)
✅ Cool bedroom temperature
✅ Avoid alcohol (suppresses deep sleep)
✅ Magnesium supplementation (consult healthcare provider)
✅ Stress management (meditation, CBT-I)
✅ Adequate total sleep duration (can't get deep sleep without sufficient opportunity)
Conclusion
Sleep tracking technology has matured into a powerful tool for understanding and optimizing one of the most critical aspects of health. While no consumer device matches clinical polysomnography, the best sleep trackers in 2026 provide actionable insights with 70-85% accuracy—sufficient for identifying patterns, tracking trends, and guiding personal optimization.
Key Takeaways:
✅ Focus on trends, not single nights: Weekly and monthly patterns matter more than daily fluctuations
✅ Consistency is critical: Regular sleep schedules improve both actual sleep quality and tracker accuracy
✅ Choose the right device for your goals: Athletes need HRV and recovery metrics; those screening for sleep disorders need SpO2 monitoring; general wellness users benefit most from comprehensive, affordable fitness bands
✅ Combine data with subjective experience: How you feel matters as much as what sensors measure
✅ Evidence-based interventions work: Cool temperatures, exercise timing, light exposure, and stress management consistently improve sleep across all metrics
✅ Know the limitations: Trackers screen and trend-track; they don't diagnose medical conditions
Sleep optimization is a marathon, not a sprint. Use your tracker data to identify opportunities, implement evidence-based changes one at a time, and give each intervention 4-6 weeks to show effects. The investment in better sleep pays dividends in every aspect of health, performance, and quality of life.
Additional Resources:
- Sleep Foundation: Comprehensive, evidence-based sleep education (sleepfoundation.org)
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Clinical sleep disorder information (aasm.org)
- CDC Sleep Guidelines: Public health recommendations (cdc.gov/sleep)
- National Sleep Foundation Sleep Diary: Free tracking template for correlating lifestyle factors with sleep quality
This guide was last updated in February 5, 2026. Sleep tracking technology evolves rapidly—check manufacturer websites for the latest features and accuracy validation studies.
Related Articles:
How Do Smart Rings Revolutionize Sleep Monitoring And OSA Risk Assessment?
Smart Band vs Smart Bracelet vs Fitness Tracker: Key Differences Explained
White Label vs OEM Wearables: Which Is the Right Choice for Your Brand?
About the Author

Kyler is a senior content marketing specialist at J-Style(Jointcorp|Joint Chinese Ltd | Youhong Medical), a leading smart ring, smart band, and smart watch manufacturer and supplier in China. With 8 years of experience in the wearable tech industry, he creates professional content for global B2B buyers seeking reliable factory, wholesale, OEM/ODM, and SDK/API solutions. At J-Style, Kyler focuses on helping partners understand the value of high-quality Chinese smart wearables and how J-Style’s innovative manufacturing capabilities support scalable business growth.






