Updated 13 hours ago
Best Smart Rings for Blood Oxygen (SpO2) Monitoring 2026: Complete Guide to Continuous Oxygen Saturation Tracking
youhong
Last Updated: February 9, 2026 | Expert Analysis of Wearable Pulse Oximetry Technology
Blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) monitoring has emerged as a critical health metric, thrust into mainstream awareness during the COVID-19 pandemic when oxygen levels became a key indicator of disease severity. What began as a clinical necessity has evolved into an essential component of comprehensive health tracking, revealing insights far beyond respiratory function—from sleep apnea detection to cardiovascular health assessment, altitude acclimatization to early illness warning.
In 2026, smart rings represent the cutting edge of continuous SpO2 monitoring technology. Unlike traditional fingertip pulse oximeters that provide single-point measurements or wrist-based devices that struggle with accuracy during sleep, smart rings combine optimal sensor placement, medical-grade technology, and 24/7 wearability to deliver hospital-quality oxygen monitoring in an elegant, unobtrusive form factor.
This comprehensive guide examines the science behind pulse oximetry, explains why smart rings excel at SpO2 monitoring, explores critical health applications from sleep apnea screening to chronic disease management, and helps you select the ideal continuous oxygen monitoring solution for your health needs.
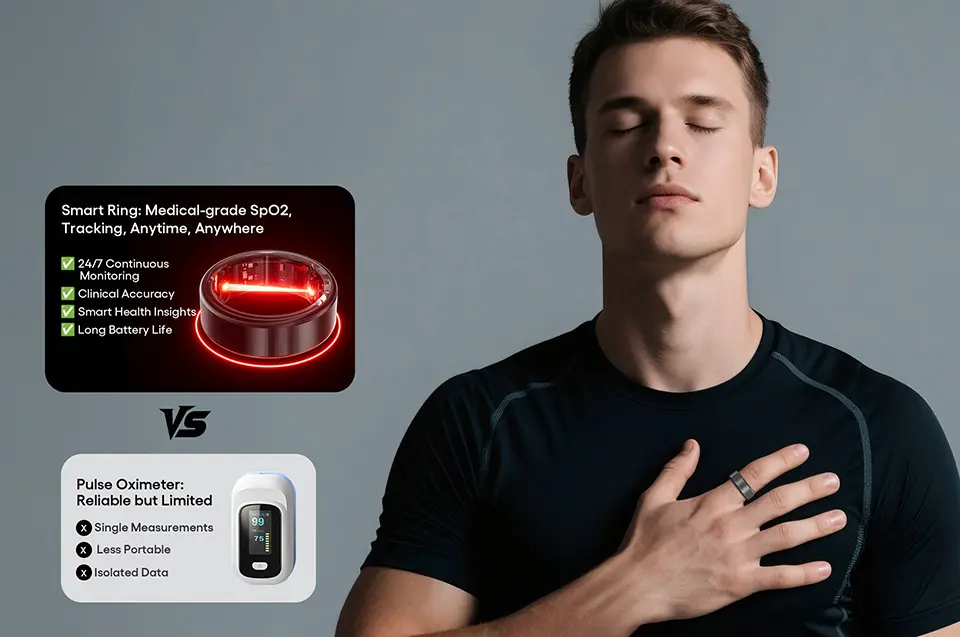

Table of Contents
- Understanding Blood Oxygen Monitoring
- Pulse Oximetry Technology Explained
- Why Smart Rings Excel at SpO2 Monitoring
- Critical Health Applications of SpO2 Tracking
- Medical-Grade vs. Consumer SpO2 Devices
- Essential Features for Continuous SpO2 Monitoring
- Sleep Apnea Detection with Smart Rings
- SpO2 Monitoring Selection Guide
- Featured Medical-Grade Solutions
- Maximizing SpO2 Data for Health Insights
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Blood Oxygen Monitoring
What is Blood Oxygen Saturation (SpO2)?
Definition:
SpO2 (peripheral oxygen saturation) measures the percentage of hemoglobin in your blood that is saturated with oxygen. Hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to tissues throughout your body.
The Measurement:
- SpO2 100%: Every hemoglobin molecule is carrying oxygen (maximum saturation)
- SpO2 95%: 95% of hemoglobin is oxygen-saturated, 5% is not
- SpO2 85%: Only 85% of hemoglobin carries oxygen (concerning level)
Normal SpO2 Ranges
Healthy Adults at Sea Level:
- Normal: 95-100%
- Borderline: 92-94% (may warrant monitoring)
- Low (Hypoxemia): <92% (medical evaluation needed)
- Critically Low: <88% (emergency medical attention)
During Sleep:
- Normal: 90-100% (brief dips to 88-90% acceptable if rare)
- Concerning: Frequent dips below 90%
- Sleep Apnea Indicator: Repeated drops to <90%, especially if >3-4% from baseline
At High Altitude:
- 8,000 feet: 92-95% normal
- 12,000 feet: 85-92% normal
- Above 14,000 feet: <85% may be normal but increases altitude sickness risk
Special Populations:
- COPD patients: May have baseline 88-92% (individual target set by physician)
- Smokers: Often 94-98% (slightly lower than non-smokers)
- Elderly: May have slightly lower baselines (93-98%)
Why SpO2 Matters for Health
Respiratory Function:
Immediate indicator of lung efficiency—how well oxygen transfers from air to blood.
Cardiovascular Health:
Low SpO2 can indicate heart problems (inefficient blood circulation even if lungs work well).
Sleep Disorders:
Repeated oxygen drops during sleep signal obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a condition affecting 22+ million Americans.
Chronic Disease Management:
- COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease): Requires continuous oxygen monitoring
- Heart failure: Low SpO2 indicates worsening condition
- COVID-19 and respiratory infections: SpO2 drops precede severe symptoms
Athletic Performance:
- Altitude training adaptations
- Recovery status (adequate oxygenation during rest)
- Overtraining detection (impaired oxygen delivery)
Early Illness Detection:
SpO2 drops often occur 1-3 days before symptomatic respiratory illness, enabling early intervention.
Pulse Oximetry vs. Arterial Blood Gas
Pulse Oximetry (SpO2):
- Non-invasive, painless
- Measures peripheral oxygen saturation
- Slightly less accurate than arterial measurement (±2-3%)
- Sufficient for screening and trend monitoring
Arterial Blood Gas (SaO2):
- Invasive (needle into artery)
- Measures actual arterial oxygen saturation
- Gold standard medical accuracy
- Used in hospitals for critical care
Clinical Acceptance:
High-quality pulse oximeters correlate 95-98% with arterial blood gas measurements—adequate for clinical decision-making in most contexts.
Pulse Oximetry Technology Explained
How Pulse Oximetry Works
Light Absorption Principle:
Oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin absorb light differently:
Red Light (660nm wavelength):
- Absorbed more by deoxygenated hemoglobin
- Passes through oxygenated blood more easily
Infrared Light (940nm wavelength):
- Absorbed more by oxygenated hemoglobin
- Passes through deoxygenated blood more easily
Measurement Process:
- LEDs emit red and infrared light through tissue
- Photodetector receives light that passes through or reflects back
- Algorithm calculates ratio of red to infrared absorption
- SpO2 percentage derived from absorption ratio using calibration curves
Pulsatile Component:
Devices measure light absorption during arterial pulsation (when blood volume increases with heartbeat) to isolate arterial blood signal from surrounding tissue.
Transmission vs. Reflectance Pulse Oximetry
Transmission (Fingertip) Method:
How It Works:
- Light source on one side of finger
- Detector on opposite side
- Light passes completely through finger tissue
Advantages:
✅ Stronger signal (light travels through arterial-rich tissue)
✅ Less affected by skin pigmentation
✅ Less affected by tissue thickness variation
✅ Medical-grade accuracy (±2% typical)
✅ Gold standard method used in hospitals
Disadvantages:
❌ Requires specific anatomy (fingertip, earlobe, toe)
❌ Traditional devices bulky and inconvenient for continuous wear
❌ Fingertip devices interfere with daily activities
Reflectance (Wrist/Ring) Method:
How It Works:
- Light source and detector on same side of tissue
- Light reflects back from tissue layers
- Measures reflected light absorption
Advantages:
✅ Can be placed anywhere with surface access
✅ Enables wrist-based and ring form factors
✅ Suitable for continuous 24/7 monitoring
✅ Unobtrusive, doesn't interfere with activities
Disadvantages:
❌ Weaker signal (light doesn't traverse full arterial bed)
❌ More affected by skin pigmentation and tissue characteristics
❌ More susceptible to motion artifacts
❌ Historically less accurate than transmission method
Modern Reflectance Technology:
Advanced algorithms, multi-wavelength LEDs, and AI signal processing have dramatically improved reflectance accuracy, with best devices approaching transmission-method performance.
Ring-Based Transmission Technology
Innovative Approach:
Modern smart rings employ transmission-style pulse oximetry despite wearable form factor:
Finger Placement Advantage:
- LEDs on inner ring surface (palm side)
- Photodetector on outer ring surface (fingernail side)
- Light transmits through finger tissue (similar to fingertip oximeters)
Why This Matters:
Signal Strength:
Transmission through finger provides strong signal comparable to medical fingertip devices.
Accuracy:
Less affected by skin tone, tissue thickness, and blood flow variations compared to wrist reflectance.
Medical-Grade Potential:
Enables clinical-accuracy SpO2 measurement in continuous wearable format.
Comfort:
Finger is natural location for transmission oximetry; ring form factor is comfortable for 24/7 wear unlike fingertip clips.
Factors Affecting SpO2 Accuracy
Physiological Factors:
Skin Pigmentation:
- Darker skin may reduce light transmission
- Can cause overestimation of SpO2 in hypoxemic states
- Quality devices compensate through calibration algorithms
- Transmission method less affected than reflectance
Nail Polish:
- Dark colors (especially blue, green, black) block light transmission
- Can cause falsely low readings or measurement failure
- Remove polish from measurement finger or use different finger
Cold Extremities:
- Vasoconstriction (narrowed blood vessels) reduces signal
- Common in cold weather, Raynaud's disease
- Warming hands improves accuracy
Motion:
- Movement creates artifacts in signal
- Advanced algorithms filter motion noise
- Ring measurements during sleep (minimal motion) are highly accurate
Anemia:
- Severe anemia (very low hemoglobin) may affect accuracy
- SpO2 may appear normal even if oxygen delivery is impaired (less hemoglobin to carry oxygen)
Environmental Factors:
Ambient Light:
- Bright light (sunlight, surgical lights) can interfere
- Quality devices use ambient light cancellation
Electromagnetic Interference:
- Rare with modern shielded devices
- MRI environments require device removal
Device Factors:
Sensor Quality:
- LED wavelength precision
- Photodetector sensitivity
- Signal processing algorithms
Calibration:
- Devices calibrated against arterial blood gas standards
- Calibration curves may vary by manufacturer
Battery Level:
- Very low battery can reduce LED intensity and accuracy
- Most devices alert before accuracy degrades

Why Smart Rings Excel at SpO2 Monitoring
Anatomical Advantages
Finger Placement Benefits:
Rich Arterial Blood Flow:
Digital arteries in fingers provide strong, pulsatile blood flow ideal for pulse oximetry.
Thin Tissue Layer:
Compared to wrist, finger tissue is thinner, allowing better light transmission.
Stable Positioning:
Ring stays in consistent position on finger (unlike wrist devices that shift during sleep).
Minimal Movement During Sleep:
Fingers move far less than wrists during sleep, reducing motion artifacts in overnight SpO2 data.
24/7 Wearability
Unobtrusive Design:
- Lightweight (3-7g typical)
- No display (no bulk)
- Doesn't interfere with clothing, keyboards, daily activities
- High overnight wear compliance (95-98% vs. 67% for smartwatches)
Comfort:
- Properly sized ring is imperceptible during sleep
- No pressure points or skin irritation common with wrist bands
- Temperature-stable (finger temperature less variable than wrist)
Continuous Monitoring Capability
24-Hour Data Collection:
Unlike fingertip pulse oximeters requiring manual spot checks, smart rings track SpO2 continuously:
Overnight Monitoring:
- Captures sleep apnea events (oxygen desaturations)
- Identifies hypoxemia patterns
- Correlates SpO2 with sleep stages
Daytime Tracking:
- Monitors response to activity, altitude
- Detects gradual SpO2 decline (early illness warning)
- Tracks recovery patterns
Trend Analysis:
- Days to weeks of historical data
- Identifies patterns invisible to spot checks
- Enables early intervention
Medical-Grade Accuracy Potential
Transmission Method:
Rings using finger transmission achieve accuracy comparable to hospital fingertip oximeters.
Clinical Validation:
Best devices undergo rigorous testing against arterial blood gas measurements across 70-100% SpO2 range.
Regulatory Approval:
Medical-grade rings may obtain regulatory clearances (FDA, CE marking) certifying clinical accuracy.
Sleep Apnea Screening Excellence
Optimal Sleep Detection:
Why Rings Outperform Wrist Devices:
- More accurate overnight SpO2 (less motion, better signal)
- Capture brief desaturation events (10-20 seconds) missed by less frequent wrist sampling
- Lower false positive/negative rates
Clinical Correlation:
Ring-based SpO2 data correlates strongly with polysomnography (sleep study) oxygen desaturation indices.
Actionable Screening:
Identifies high-risk individuals who should pursue formal sleep study for diagnosis.

Critical Health Applications of SpO2 Tracking
1. Sleep Apnea Screening and Monitoring
What is Sleep Apnea?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA):
Upper airway collapses during sleep → breathing stops → oxygen drops → brain arouses to reopen airway → cycle repeats (often hundreds of times per night).
Prevalence:
- ~22 million Americans have OSA
- 80% of moderate-severe cases are undiagnosed
- More common in men, older adults, obese individuals
Health Consequences:
- Cardiovascular: Hypertension, heart attack, stroke, atrial fibrillation
- Metabolic: Diabetes, insulin resistance, weight gain
- Cognitive: Impaired concentration, memory problems, mood disorders
- Safety: Drowsy driving accidents (7x higher risk)
- Quality of life: Chronic fatigue, relationship problems (snoring)
How Smart Rings Detect Sleep Apnea:
Oxygen Desaturation Index (ODI):
Number of times SpO2 drops ≥3% or ≥4% from baseline per hour of sleep.
Classification:
- ODI <5: Normal
- ODI 5-15: Mild sleep apnea
- ODI 15-30: Moderate sleep apnea
- ODI >30: Severe sleep apnea
Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) Correlation:
Ring-derived ODI correlates strongly with clinical AHI (gold standard from sleep study).
Smart Ring Sleep Apnea Screening Process:
Multi-Night Data Collection:
- Minimum 3 consecutive nights recommended
- Captures night-to-night variability
- Increases accuracy
Algorithm Analysis:
- Identifies oxygen desaturation events
- Calculates ODI
- Assesses desaturation patterns (duration, frequency, depth)
- Generates risk assessment
Risk Stratification:
- Low risk (ODI <5): Normal, continue periodic monitoring
- Moderate risk (ODI 5-15): Discuss with physician, consider lifestyle modifications
- High risk (ODI >15): Formal sleep study recommended
Clinical Value:
Early Detection:
Identifies asymptomatic individuals (many people don't realize they have apnea).
Monitoring Treatment:
- Tracks CPAP therapy effectiveness (oxygen levels should normalize with proper treatment)
- Detects CPAP non-adherence or equipment problems
- Monitors oral appliance effectiveness
Avoids Unnecessary Sleep Studies:
Low-risk individuals may not need expensive formal testing.
2. Chronic Respiratory Disease Management
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease):
Monitoring Goals:
- Baseline SpO2 tracking
- Early detection of exacerbations (worsening episodes)
- Oxygen therapy effectiveness
How Smart Rings Help:
Baseline Establishment:
Many COPD patients have lower baseline SpO2 (88-92% common). Ring establishes personal normal.
Exacerbation Detection:
SpO2 drop of 3-5% from baseline often precedes symptomatic COPD exacerbation by 1-3 days.
Early Intervention:
Enables increased medications, oxygen therapy, or medical contact before crisis.
Evidence:
Studies show continuous SpO2 monitoring reduces COPD hospitalizations by 20-30% through early intervention.
Asthma:Nocturnal Oxygen Monitoring:
Some asthma patients experience nocturnal hypoxemia (low oxygen during sleep) without awareness.
Trigger Identification:
Correlate SpO2 drops with environmental factors, activities, or allergen exposures.
Medication Effectiveness:
Track whether controller medications maintain normal overnight oxygenation.
Interstitial Lung Disease:
Progressive Monitoring:
Track gradual SpO2 decline over months, indicating disease progression.
Oxygen Therapy Titration:
Verify prescribed oxygen levels maintain target SpO2.
3. Cardiovascular Disease Detection
Heart Failure:
Relationship:
Heart failure → inefficient blood circulation → inadequate oxygen delivery → low SpO2 (even if lungs are healthy).
Decompensation Warning:
Worsening heart failure often shows as declining SpO2 days before symptomatic edema (fluid buildup) or shortness of breath.
Monitoring Strategy:
- Baseline SpO2 when stable
- Alert physician if sustained 3-5% drop
- Enables medication adjustment before crisis
Pulmonary Hypertension:
SpO2 During Activity:
Exertional hypoxemia (SpO2 drops during activity but normal at rest) is hallmark finding.
Sleep Monitoring:
Nocturnal hypoxemia common in pulmonary hypertension.
Atrial Fibrillation:
Indirect Association:
AFib can reduce cardiac output → lower SpO2 in some patients.
Sleep Apnea Connection:
OSA (detectable via SpO2 monitoring) increases AFib risk 4-5x.
4. COVID-19 and Respiratory Infection Monitoring
Silent Hypoxemia:
COVID-19 Discovery:
Many COVID-19 patients had dangerously low SpO2 (<90%) without feeling short of breath—termed "silent" or "happy" hypoxemia.
Early Detection:
Continuous SpO2 monitoring detects oxygen decline before patient feels unwell.
Triage Decision:
Helps determine who needs hospital admission vs. home monitoring.
Home Monitoring Protocols:
Quarantine Surveillance:
COVID-positive individuals monitor SpO2 at home; alert physician if <94%.
Post-Infection Recovery:
Track SpO2 normalization (long COVID patients may have persistent low SpO2).
Future Pandemic Preparedness:
Continuous SpO2 monitoring provides early warning system for respiratory illness outbreaks.
5. Altitude Acclimatization
High-Altitude Physiology:
Reduced Oxygen Availability:
As altitude increases, atmospheric pressure decreases → less oxygen enters bloodstream → lower SpO2.
Acclimatization Process:
Over days-weeks at altitude, body adapts:
- Increased breathing rate
- Increased red blood cell production
- Improved oxygen utilization
- SpO2 gradually improves (but remains below sea level)
Smart Ring Applications:
Monitoring Ascent:
- Track SpO2 at each altitude stage
- Identify individuals not acclimatizing properly (SpO2 remains very low)
- Inform pace of ascent (slower if SpO2 doesn't recover)
Altitude Sickness Risk:
- Very low SpO2 (<75% at high altitude) increases acute mountain sickness risk
- Overnight monitoring (SpO2 should recover during sleep; failure suggests inadequate acclimatization)
Descent Decisions:
If SpO2 remains critically low despite rest and hydration, descent is necessary.
Athletic Training:
Altitude Training Camps:
Athletes track acclimatization progress via SpO2 trends.
"Live High, Train Low" Monitoring:
Verify adequate overnight oxygenation at altitude while training at lower elevations.
6. Women's Health: Pregnancy and Fertility
Pregnancy Monitoring:
Gestational Changes:
Pregnant women require ~20% more oxygen; SpO2 should remain normal but requires adequate iron stores.
High-Risk Pregnancies:
- Preeclampsia can affect oxygenation
- Pregnancy-related heart conditions may reduce SpO2
- Continuous monitoring provides reassurance or early warning
Sleep-Disordered Breathing:
Pregnancy increases sleep apnea risk; SpO2 monitoring screens for this.
Fertility and Cycle Tracking:
Temperature + SpO2:
Some smart rings combine body temperature (for ovulation detection) with SpO2 (overall health marker).
Oxygenation and Fertility:
Adequate tissue oxygenation supports reproductive health; chronic hypoxemia may affect fertility.
7. Metabolic and Chronic Disease Integration
Diabetes Management:
Hypoglycemia Detection:
Severe low blood sugar can cause confusion, altered consciousness, and sometimes slight SpO2 decrease (from reduced circulation).
Diabetic Complications:
- Peripheral vascular disease → poor circulation → lower extremity SpO2
- Diabetic neuropathy → sleep-disordered breathing → oxygen desaturations
Integration with CGM:
Combining continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) with SpO2 provides comprehensive metabolic picture.
Multi-Parameter Chronic Disease Platforms:
Hospital-at-Home Models:
Patients recovering from surgery or managing chronic conditions upload:
- SpO2 data
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Glucose (if diabetic)
- Symptoms
Remote Physician Monitoring:
Care teams review data dashboards, intervening when parameters exceed thresholds.
Reduces Hospitalizations:
Early detection and intervention prevent emergency admissions.
Medical-Grade vs. Consumer SpO2 Devices
Regulatory Classifications
Medical-Grade Devices:
FDA Clearance (United States):
- Class II medical device designation
- 510(k) clearance requires clinical validation
- Performance standards: ±2-3% accuracy across 70-100% SpO2 range
- Manufacturing quality controls (ISO 13485)
- Can be used for clinical decision-making
CE Marking (Europe):
- Medical Device Regulation (MDR) compliance
- Clinical evaluation and performance testing required
- Notified body assessment
Clinical Validation Requirements:
- Testing against arterial blood gas (gold standard)
- Minimum 10-12 subjects
- SpO2 range 70-100% tested
- Diverse skin pigmentation represented
- Statistical analysis demonstrating accuracy
Consumer Wellness Devices:
No Medical Claims:
- Marketed for "general wellness" or "fitness"
- Not intended for medical diagnosis or treatment decisions
- No FDA clearance or CE medical marking
- Accuracy may be lower and untested
Variable Quality:
Some consumer devices perform well; others are unreliable. Without validation data, accuracy is unknown.
Accuracy Standards Comparison
Medical-Grade Standard:
- Target: ±2% across 70-100% SpO2
- Validation: Clinical study against arterial blood gas
- Example: If true SpO2 is 95%, device reads 93-97%
High-Quality Consumer Standard:
- Target: ±3-4% across 90-100% SpO2
- Validation: May compare to medical fingertip oximeter (not arterial blood gas)
- Example: If true SpO2 is 95%, device reads 91-99%
Low-Quality Consumer:
- Accuracy: Unknown, untested, or ±5-10%
- Validation: None or insufficient
- Risk: May miss dangerous hypoxemia or create false alarms
When Medical-Grade Matters
Critical Applications:
Required for Clinical Decisions:
✅ COPD monitoring and oxygen therapy titration
✅ Heart failure management
✅ Post-surgical monitoring
✅ COVID-19 home monitoring protocols
✅ Newborn/infant monitoring
✅ Any scenario where physician makes treatment decisions based on SpO2
Acceptable Consumer-Grade:
✅ Sleep apnea screening (confirmation via formal sleep study before treatment)
✅ Altitude acclimatization tracking
✅ General wellness monitoring
✅ Fitness/athletic performance
✅ Personal health awareness
Recommendation:
If you have respiratory or cardiovascular disease, prioritize medical-grade devices. For general wellness and screening, high-quality consumer devices with published validation are acceptable.

Essential Features for Continuous SpO2 Monitoring
Core Features (Must-Have)
1. Continuous 24/7 Monitoring
✅ Automatic background SpO2 measurement (no manual activation)
✅ Overnight tracking (captures sleep apnea events)
✅ Frequent sampling (every 1-5 minutes minimum; every 30-60 seconds ideal)
✅ Trend data storage (minimum 7 days; 30+ days preferred)
2. Oxygen Desaturation Event Detection
✅ Identifies when SpO2 drops ≥3-4% from baseline
✅ Counts desaturation events per hour (ODI calculation)
✅ Records event duration and severity
✅ Differentiates brief artifacts from true hypoxemic events
3. Baseline and Trend Analysis
✅ Establishes personal SpO2 baseline over days-weeks
✅ Identifies deviations from baseline
✅ Visual graphs showing SpO2 over time (hourly, nightly, weekly)
✅ Sleep vs. wake SpO2 comparison
4. Low SpO2 Alerts
✅ Customizable threshold (e.g., alert if <90% for >1 minute)
✅ Real-time notifications (vibration or smartphone alert)
✅ Urgent vs. informational alert levels
✅ Alert history logging
5. Medical-Grade Accuracy
✅ Published clinical validation data
✅ FDA/CE medical device certification (if claiming medical use)
✅ ±2-3% accuracy specification
✅ Testing across diverse populations (skin tones, ages)
Advanced Features (Differentiators)
6. Sleep Apnea Risk Assessment
✅ Multi-night data collection (3+ nights)
✅ AHI or ODI calculation
✅ Risk stratification (low/moderate/high)
✅ Educational content explaining sleep apnea
✅ Physician-shareable reports
7. Data Export and Medical Sharing
✅ PDF reports with SpO2 graphs and statistics
✅ CSV or compatible data export
✅ HIPAA-compliant data transmission (if applicable)
✅ Direct integration with healthcare provider systems
8. Multi-Parameter Integration
✅ Combines SpO2 with heart rate (bradycardia during apneas)
✅ Respiratory rate tracking (breathing pauses)
✅ Sleep stage correlation (desaturations often in REM sleep)
✅ Body temperature (illness detection)
9. Activity and Altitude Correlation
✅ Tracks SpO2 during exercise vs. rest
✅ Altitude detection and acclimatization tracking
✅ Identifies exertional hypoxemia (SpO2 drops with activity)
10. Long-Term Trend Intelligence
✅ Week-over-week comparison
✅ Seasonal variation tracking
✅ Medication/treatment effect monitoring
✅ Predictive alerts (AI detects gradual SpO2 decline)
User Experience Features
11. Comfortable 24/7 Wear
✅ Lightweight (<7g for rings)
✅ Hypoallergenic materials
✅ Proper sizing (rings especially critical)
✅ No sharp edges or discomfort during sleep
12. Long Battery Life
✅ Minimum 5 days with continuous SpO2 monitoring
✅ 7-10 days ideal
✅ Battery level indicator
✅ Fast charging (1-2 hours)
13. Water Resistance
✅ 5 ATM (50m) minimum
✅ Allows handwashing, showering without removal
✅ Maintains sensor accuracy when wet
14. Intuitive App Interface
✅ Clear SpO2 visualization
✅ Easy-to-understand metrics
✅ Educational content
✅ Actionable recommendations
✅ Historical data review
Clinical and Research Features
15. API Access for Integration
✅ Developer API for third-party app integration
✅ Healthcare system integration (EHR compatibility)
✅ Research data export
✅ Family member data sharing (caregiver access)
16. Regulatory Compliance
✅ FDA 510(k) clearance or equivalent
✅ CE medical device marking
✅ ISO 13485 manufacturing certification
✅ Regular firmware updates maintaining accuracy
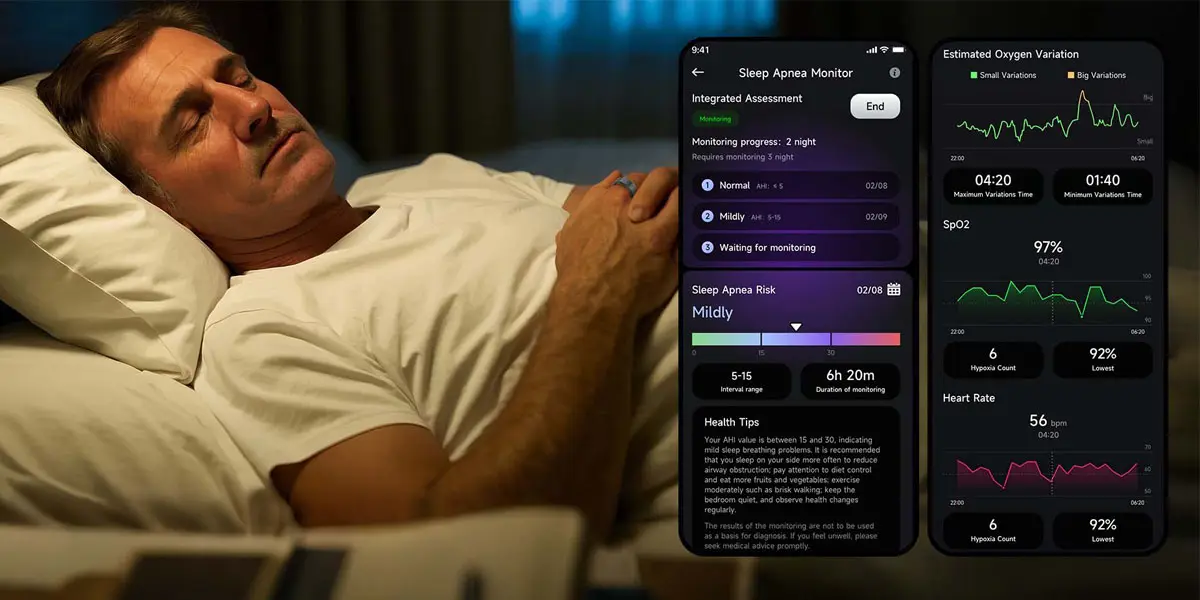
Sleep Apnea Detection with Smart Rings
Clinical Context
The Problem:
- 22 million Americans have obstructive sleep apnea
- 80% of moderate-severe cases undiagnosed
- Barriers: Expensive sleep studies, limited sleep lab availability, inconvenience
The Opportunity:
Home screening with continuous SpO2 monitoring identifies high-risk individuals for formal diagnosis and treatment.
How Ring-Based Sleep Apnea Screening Works
Multi-Night Protocol:
Night 1-3: Data Collection
- Wear ring during normal sleep
- Device automatically tracks SpO2 continuously
- No user intervention required
Algorithm Analysis:
- Identifies oxygen desaturation events (≥3% or ≥4% drops)
- Calculates Oxygen Desaturation Index (ODI): events per hour
- Assesses desaturation severity (depth and duration)
- Analyzes patterns (clusters in REM sleep typical for OSA)
Report Generation:
- ODI score
- Total desaturation events
- Average/minimum overnight SpO2
- Risk assessment (low/moderate/high)
Understanding Sleep Apnea Definitions
What is a Sleep Apnea Event?
Apnea:
Complete cessation of breathing for ≥10 seconds.
Hypopnea:
Partial reduction in breathing (30-90% reduction) for ≥10 seconds with oxygen desaturation or arousal.
Mechanism in Obstructive Sleep Apnea:
- Throat muscles relax during sleep
- Upper airway (pharynx) collapses
- Breathing stops despite chest/abdomen effort to breathe
- Oxygen level drops
- Brain arouses (often not to full consciousness) to reopen airway
- Breathing resumes, often with gasp or snort
- Cycle repeats—sometimes hundreds of times per night
Symptoms and Health Risks
Symptoms:
Nighttime:
- Loud snoring
- Witnessed breathing pauses (observed by bed partner)
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Frequent awakenings
- Restless sleep
Daytime:
- Excessive sleepiness
- Morning headaches
- Difficulty concentrating
- Memory problems
- Irritability, mood changes
- Decreased libido
Long-Term Health Consequences:
Cardiovascular:
- Hypertension (60-70% of OSA patients have high blood pressure)
- Heart attack risk increased 30%
- Stroke risk increased 60%
- Atrial fibrillation risk increased 4-5x
- Heart failure
Metabolic:
- Type 2 diabetes risk increased
- Weight gain (fatigue reduces activity)
- Metabolic syndrome
Cognitive:
- Increased dementia risk
- Impaired executive function
- Depression and anxiety
Safety:
- Motor vehicle accidents (drowsy driving)
- Workplace accidents
- Reduced quality of life
AHI Classification and Severity
Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI):
Number of apneas + hypopneas per hour of sleep (gold standard from polysomnography).
Severity:
- Normal: AHI <5
- Mild OSA: AHI 5-15
- Moderate OSA: AHI 15-30
- Severe OSA: AHI >30
ODI Correlation:
Oxygen Desaturation Index (from smart ring) correlates strongly with AHI:
- High ODI → likely high AHI
- Low ODI → likely low AHI (but not 100% exclusion—some OSA causes arousals without large oxygen drops)
When to Pursue Formal Sleep Study
High-Risk Ring Screening:
- ODI >15 (moderate-high risk)
- Frequent deep desaturations (<85%)
- Symptomatic (snoring, daytime sleepiness, witnessed apneas)
Action:
Discuss with physician → Referral to sleep medicine → Home sleep apnea test or in-lab polysomnography → Diagnosis → Treatment (CPAP, oral appliance, surgery, or lifestyle modification)
Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness
CPAP Therapy:
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure keeps airway open mechanically.
Ring Monitoring:
- Baseline: High ODI, low overnight SpO2
- On CPAP: ODI should normalize (<5), SpO2 should remain >90-95% throughout night
- Non-adherence detection: If user doesn't wear CPAP, ring shows persistent high ODI
- Equipment problems: Leak or incorrect pressure shows partial improvement but persistent desaturations
Oral Appliances:
Mandibular Advancement Devices reposition jaw to open airway.
Ring Monitoring:
- Tracks whether appliance reduces oxygen desaturations
- Less effective than CPAP for severe OSA; ring data shows if adequate treatment achieved
Weight Loss and Lifestyle:
Obesity is major OSA risk factor; weight loss can reduce severity.
Ring Monitoring:
- Tracks ODI improvement over months as weight decreases
- Motivates adherence (seeing objective improvement)
SpO2 Monitoring Selection Guide
Step 1: Define Your Primary Goal
Medical Monitoring:
- Managing diagnosed respiratory/cardiac condition
- Physician-recommended SpO2 tracking
- → Requires medical-grade device with FDA/CE clearance
Sleep Apnea Screening:
- Symptoms suggest possible OSA
- High risk (obesity, age >50, male, family history)
- → Requires accurate overnight monitoring with sleep apnea algorithm
Altitude/Athletic Performance:
- High-altitude travel or training
- Endurance athlete monitoring recovery
- → Consumer-grade acceptable; prioritize continuous tracking and trends
General Wellness:
- Health-conscious monitoring
- COVID-19 or illness early detection
- → Consumer-grade acceptable; prioritize ease of use and integration
Step 2: Assess Accuracy Requirements
Medical-Grade Needed:
- COPD, heart failure, pulmonary hypertension
- Post-operative monitoring
- Oxygen therapy titration
- → Require ±2-3% accuracy, FDA/CE clearance
High-Quality Consumer Acceptable:
- Sleep apnea screening (formal diagnosis required anyway)
- Wellness tracking
- → ±3-4% accuracy adequate
Validation Verification:
- Check for published clinical studies
- Look for comparison to arterial blood gas or medical-grade oximeters
- Verify testing across 70-100% SpO2 range
Step 3: Ring vs. Wrist Device
Smart Ring Advantages:
✅ Superior overnight accuracy (less motion, better finger signal)
✅ More comfortable for sleep (98% compliance vs. 67% wrist)
✅ Transmission-based sensors possible (medical-grade accuracy)
✅ Doesn't interfere with daily activities
✅ Better for sleep apnea screening specifically
Smart Ring Disadvantages:
❌ No display (must check phone for data)
❌ Fixed sizing (must order correct size)
❌ Higher cost ($200-500 typical)
❌ Limited activity tracking during workouts
Wrist Device Advantages:
✅ Built-in display (glanceable SpO2)
✅ Comprehensive fitness tracking
✅ Adjustable fit
✅ Lower cost options available
Wrist Device Disadvantages:
❌ Lower overnight accuracy (motion, weaker reflectance signal)
❌ Less comfortable for 24/7 wear
❌ Bulkier
Recommendation for SpO2 Priority:
Smart ring if sleep apnea screening or overnight monitoring is primary goal. Wrist device if you want all-in-one fitness + wellness tracking and SpO2 is secondary feature.
Step 4: Feature Prioritization
| Priority Level | User Profile | Critical Features |
| Medical | Diagnosed respiratory/cardiac condition | FDA/CE clearance, continuous monitoring, data export, low SpO2 alerts |
| Sleep Apnea Screening | Suspected OSA, high risk | Overnight tracking, ODI calculation, multi-night analysis, physician reports |
| Altitude/Athletic | Mountaineering, endurance training | Continuous tracking, trend analysis, activity correlation |
| General Wellness | Health awareness, illness detection | Reliable accuracy, user-friendly app, long battery |
Step 5: Budget Considerations
Budget Tier (100-200):
- Consumer-grade SpO2
- Limited validation data
- Basic overnight tracking
- Best for: General wellness awareness
Mid-Range Tier (200-350):
- High-quality sensors
- Published validation studies
- Sleep apnea screening algorithms
- Good accuracy (±3-4%)
- Best for: Most users prioritizing SpO2
Premium Tier (350-600):
- Medical-grade certification (FDA/CE)
- Clinical accuracy (±2-3%)
- Comprehensive health platform integration
- Advanced AI analytics
- Best for: Medical monitoring, serious health optimization
Step 6: Ecosystem and Data Integration
App Quality:
✅ Clear SpO2 visualization
✅ Educational content
✅ Trend analysis tools
✅ Export capabilities
Platform Integration:
✅ Apple Health / Google Fit sync
✅ Third-party health apps
✅ Electronic health record (EHR) integration for medical use
✅ Family member sharing (caregiver access)
Data Ownership:
✅ Can export your data
✅ No mandatory subscription for core features
✅ Privacy protections (HIPAA compliance if medical device)
Featured Medical-Grade Solutions
The smart ring SpO2 monitoring market has advanced significantly, with several devices now offering medical-grade accuracy in elegant wearable form factors. Below is an example representing the current state-of-the-art in continuous oxygen saturation tracking.
Medical-Grade Smart Rings: Transmission Pulse Oximetry Technology
Modern medical-grade smart rings employ sophisticated transmission-based pulse oximetry, the same fundamental technology used in hospital fingertip devices, adapted into a continuous-wear ring form factor.
Transmission vs. Reflectance Technology:
Why Transmission Matters:
Stronger Signal:
Light travels completely through finger tissue (palm to fingernail side), traversing arterial-rich tissue for robust oxygen saturation measurement.
Reduced Interference:
Less affected by:
- Skin pigmentation (melanin content)
- Tissue thickness variations
- Surface blood flow fluctuations
Medical-Grade Accuracy:
Transmission method achieves ±2-3% accuracy comparable to clinical fingertip pulse oximeters.
Scientific Basis:
Transmission pulse oximetry mirrors the gold-standard fingertip clip oximeters used extensively during the COVID-19 pandemic and in hospital settings worldwide.
Clinical Validation and Certification:
Rigorous Testing Standards:
Medical-grade smart rings undergo comprehensive clinical validation:
Testing Protocol:
- Comparison to arterial blood gas measurements (gold standard)
- SpO2 range tested: 70-100% (covers normal to severely hypoxemic states)
- Diverse participant populations (age, gender, skin tone)
- Statistical analysis of accuracy
Performance Metrics:
- Maximum allowable error: ±4.0% (medical standard)
- Best devices achieve: ±2.7% actual error (exceeds standard)
- Consistent accuracy across full measurement range
Regulatory Approvals:
- FDA 510(k) clearance (United States medical device approval)
- CE marking (European medical device certification)
- ISO 13485 manufacturing quality management
Clinical Acceptance:
Data quality suitable for:
- Physician clinical decision-making
- Treatment monitoring
- Remote patient management programs
- Hospital-at-home protocols
Continuous 24/7 Monitoring Capabilities:
Automatic Background Tracking:
No User Action Required:
Ring continuously monitors SpO2 throughout day and night without manual activation.
Overnight Sleep Monitoring:
Captures complete sleep period including:
- Baseline overnight SpO2
- Oxygen desaturation events
- Event frequency, duration, and severity
- Correlation with sleep stages
Daytime Surveillance:
- Activity-related SpO2 changes
- Exertional hypoxemia detection
- Gradual baseline shifts (early illness warning)
- Altitude acclimatization tracking
Advanced Sleep Apnea Screening:
Comprehensive OSA Risk Assessment:
Multi-Night Data Collection:
Minimum 3 consecutive nights of sleep data recommended for accurate assessment (captures night-to-night variability).
Oxygen Desaturation Analysis:
- Identifies events where SpO2 drops ≥3-4% from baseline
- Calculates Oxygen Desaturation Index (ODI): events per hour
- Classifies severity: Normal (<5), Mild (5-15), Moderate (15-30), Severe (>30)
Educational Framework:
Comprehensive in-app explanations:
Sleep Apnea Definition:
Clear description of obstructive sleep apnea mechanism (upper airway collapse).
Symptoms:
- Nighttime: Snoring, breathing pauses, restless sleep
- Daytime: Excessive sleepiness, poor concentration, morning headaches
Health Risks:
Long-term consequences including:
- Hypertension
- Cardiovascular disease (heart attack, stroke risk)
- Metabolic disorders
- Cognitive impairment
AHI Index Education:
Explanation of severity classification based on Apnea-Hypopnea Index.
Actionable Recommendations:
Guidance on when to seek medical evaluation based on screening results.
AI-Powered Health Management Integration:
Intelligent Health Coaching System:
AI Coach:
Personalized lifestyle guidance based on real-time physiological data including SpO2, providing:
- Preventive health recommendations
- Behavior modification suggestions
- Activity and rest optimization
AI Insight:
Predictive analytics identifying patterns and trends:
- Early warning of declining health metrics
- Correlation between lifestyle factors and SpO2
- Long-term health trajectory predictions
Comprehensive Multi-Parameter Health Tracking:
Cardiovascular Monitoring:
- Continuous heart rate tracking
- Heart rate variability (HRV) analysis
- Abnormal heart rate alerts
- Cardiac health trend analysis
Sleep Architecture:
- Sleep stage detection (deep, light, REM, wake)
- Sleep quality scoring
- Recovery assessment
- Sleep debt calculation
Vital Age Assessment:
Biological age estimation based on multi-dimensional health indicators:
- Cardiovascular fitness
- Sleep quality
- Recovery patterns
- Activity levels
- Stress markers
Reveals whether physiological function is younger or older than chronological age.
Body Recovery Index:
Daily readiness score combining:
- Overnight SpO2 patterns
- HRV recovery
- Sleep quality
- Resting heart rate normalization
Guides daily activity intensity decisions.
Women's Health Specialization:
Precision Cycle Tracking:
AI algorithms predict:
- Menstrual cycle timing
- Ovulation window
- Fertile period
Medical-Grade Temperature Monitoring:
High-precision body temperature sensor enables:
- Basal body temperature tracking (fertility)
- Ovulation confirmation (temperature shift)
- Early illness detection (fever warning)
- Hormonal balance assessment
Pregnancy Support:
Continuous health monitoring throughout pregnancy including oxygen saturation (ensuring maternal-fetal oxygenation).
Chronic Disease Management Platform:
CGM Integration (Continuous Glucose Monitoring):
For diabetes patients, integration with CGM devices creates comprehensive metabolic dashboard:
- Blood oxygen (tissue oxygenation)
- Blood glucose (metabolic control)
- Heart rate and HRV (autonomic function)
- Sleep quality (affects both glucose and oxygenation)
Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Risk Assessment:
Advanced AI Algorithm:
Proprietary algorithm developed with international research teams analyzes PPG (photoplethysmography) raw data to estimate blood glucose fluctuation risk.
How It Works:
- PPG signal contains information about blood flow, vessel elasticity, autonomic regulation
- AI trained on thousands of individuals correlates PPG patterns with glucose levels
- Cloud-based processing generates glucose risk trends
Applications:
- Diabetes risk early warning
- Metabolic pattern identification
- Glucose variability trend analysis
- Lifestyle intervention guidance
Important Note:
This is risk assessment, not direct glucose measurement. Diabetics still require fingerstick or CGM for treatment decisions.
Remote Patient Monitoring Infrastructure:
Hospital-at-Home Integration:
Use Case Example:
Diabetic patient with cardiovascular comorbidities:
Monitored Parameters:
- Overnight SpO2 (detects nocturnal hypoxemia, sleep apnea)
- Sleep quality (affects glucose control and cardiovascular health)
- Heart rate and HRV (cardiovascular status, autonomic neuropathy)
- Optional: CGM glucose data integration
Data Flow:
- Ring continuously collects physiological data
- Bluetooth sync to smartphone app
- Cloud platform processes data with AI algorithms
- Data dashboard accessible to medical team
- Alerts generated for out-of-range parameters
- Physician can remotely intervene (medication adjustment, patient contact, schedule visit)
Benefits:
- Reduces hospital readmissions
- Enables early intervention before crisis
- Improves patient outcomes
- Lowers healthcare costs
- Increases patient engagement and self-management
Family Health Sharing:
Member Health Feature:
Caregivers can monitor family members' health data:
- Elderly parent monitoring (detecting health decline)
- Chronic disease patient oversight
- Post-surgical recovery tracking
- Peace of mind for distant family members
Privacy Controls:
User grants specific data access permissions.
Enterprise and Healthcare System Integration:
API and SDK Availability:
Capabilities:
- Server-to-server data transfer
- Integration with custom healthcare platforms
- Electronic health record (EHR) compatibility
- Research data collection
Use Cases:
- Corporate wellness programs
- Clinical research studies
- Remote patient monitoring programs
- Population health management
Example: JCRing X3 Medical-Grade Smart Ring
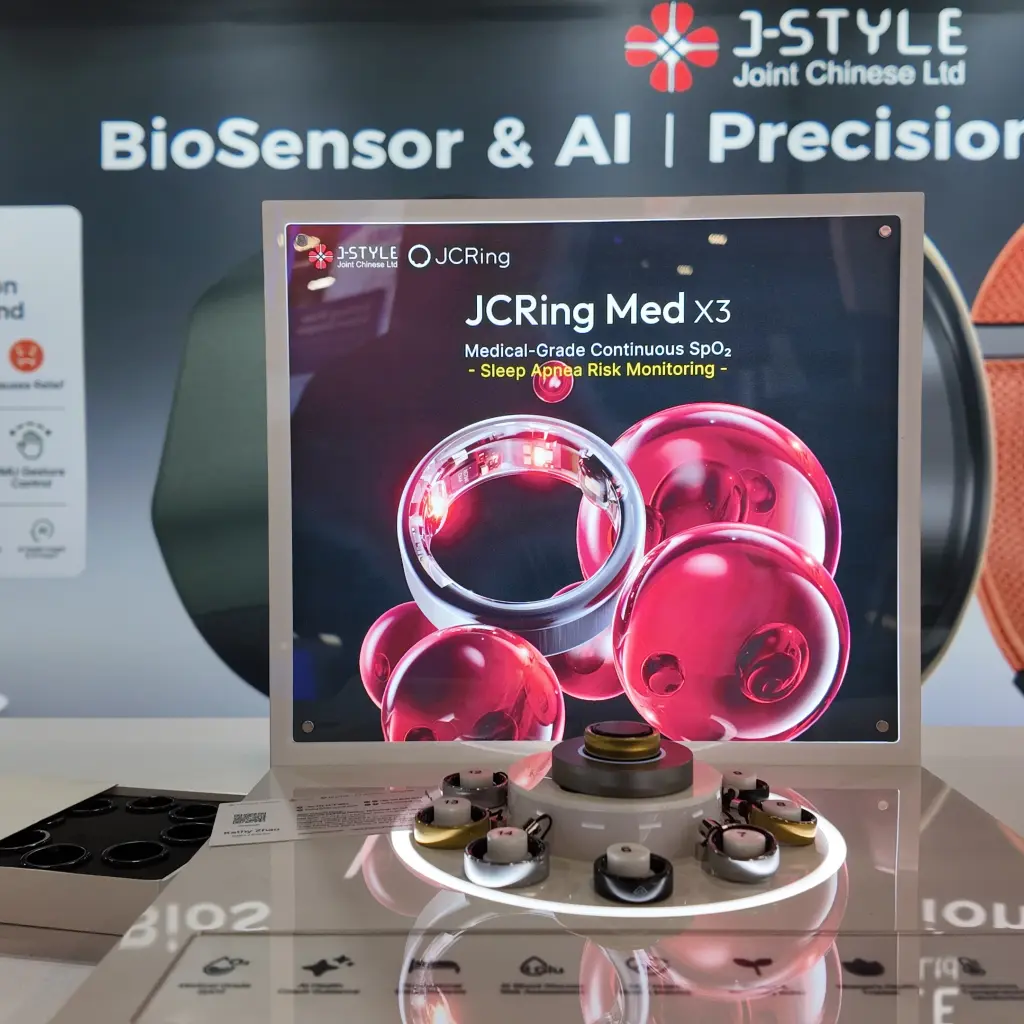
The JCRing X3 Blood Oxygen Smart Ring exemplifies medical-grade continuous SpO2 monitoring in smart ring format:
Medical-Grade SpO2 Technology:
- Transmission-based pulse oximetry (stronger signal, medical-grade accuracy)
- Clinical validation: Tested 70-100% SpO2 range, ±2.7% maximum error
- China Clinical Medical Device Certification Equipment
Comprehensive Sleep Apnea Screening:
- Multi-night data collection (3+ nights recommended)
- ODI calculation and AHI correlation
- Risk stratification with educational content
- Physician-shareable reports
AI Health Management:
- AI Coach for personalized lifestyle guidance
- AI Insight for predictive health analytics
- Vital Age biological age assessment
- Recovery index for daily readiness
Integrated Health Platform:
- Cardiovascular monitoring (HR, HRV, abnormal rate alerts)
- Sleep architecture analysis
- Women's health (cycle prediction, temperature tracking)
- CGM integration for diabetes management
- Non-invasive glucose risk assessment algorithm
Enterprise Features:
- API/SDK for system integration
- Family member health sharing
- Remote patient monitoring compatibility
- Apple Health and Google Fit synchronization
Extended Battery Life:
7-10 days continuous monitoring (Note: Sleep apnea screening and other intensive features increase power consumption; ensure >50% battery for overnight monitoring sessions).
This represents the current frontier of medical-grade wearable SpO2 monitoring—professional accuracy in a comfortable, continuous-wear form factor with intelligent health insights.
Key Selection Considerations
Transmission Technology Priority:
For medical-grade accuracy, prioritize rings using transmission pulse oximetry over reflectance methods.
Clinical Validation Evidence:
Require published testing data showing accuracy compared to arterial blood gas across full SpO2 range (70-100%).
Regulatory Certification:
FDA 510(k) or CE medical device marking confirms independent validation and quality standards.
Comprehensive Platform:
Best value comes from devices integrating SpO2 with other vital signs (HR, HRV, temperature, sleep) for holistic health picture.
No Subscription Model:
Devices offering full functionality without ongoing subscriptions provide better long-term value, especially for medical features.

Maximizing SpO2 Data for Health Insights
Establishing Your Personal Baseline
Why Baselines Matter:
Individual SpO2 varies based on:
- Altitude (lower at high elevation)
- Lung health (COPD patients may have 88-92% baseline)
- Age (slight decline with age)
- Fitness level
- Smoking history
Baseline Establishment Period:
Week 1-2:
- Wear device continuously
- Normal activities and sleep
- Device learns your patterns
Week 3-4:
- Personal baseline emerges
- Overnight SpO2 average identified
- Daytime variations mapped
Meaningful Deviation Thresholds:
SpO2 Drop of 3-5% from baseline:
- For 1-2 nights: Monitor, may be transient (nasal congestion, sleeping position)
- For 3+ nights: Investigate cause, consider medical consultation
SpO2 Drop of >5% sustained:
- Medical evaluation recommended
- Possible respiratory infection, worsening chronic condition, new cardiac issue
Interpreting Overnight SpO2 Patterns
Normal Overnight Pattern:
Characteristics:
- SpO2 stable 95-100% throughout night
- Brief dips to 90-92% acceptable if rare (<2-3 per night)
- Gradual 1-2% decrease during REM sleep normal
Sleep Apnea Pattern:
Characteristics:
- Cyclic oxygen desaturations (sawtooth pattern)
- Dips to 85-90% or lower
- Frequent events (>5 per hour)
- Clusters during REM sleep common (REM-related OSA)
Example:
Baseline 96% → drops to 88% for 15-30 seconds → rapidly returns to 95-96% → repeats cyclically throughout night
Action:
- ODI >15: High-priority sleep medicine referral
- ODI 5-15: Discuss with physician, lifestyle modifications
- ODI <5 but symptomatic: May have central sleep apnea or other sleep disorder—formal sleep study warranted
Illness Pattern:
Characteristics:
- Gradual overall decrease in baseline overnight SpO2
- Sustained low levels (92-94% when normally 96-98%)
- Often precedes symptomatic respiratory infection by 1-2 days
Action:
- Rest, hydration, immune support
- Monitor progression
- Medical contact if SpO2 <92% sustained or declining
Activity and Exertional SpO2
Normal Response to Exercise:
Healthy Individuals:
- SpO2 remains >95% during light-moderate exercise
- Brief dips to 92-94% during maximum exertion acceptable
- Rapid return to baseline within 1-2 minutes post-exercise
Exertional Hypoxemia (Abnormal):
Characteristics:
- SpO2 drops to <90% during moderate exercise
- Slow recovery post-exercise (>5 minutes to baseline)
- Breathlessness disproportionate to activity
Possible Causes:
- Interstitial lung disease
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Heart failure
- Severe deconditioning
- High-altitude inadequate acclimatization
Action:
Medical evaluation recommended—exercise-induced hypoxemia warrants workup.
Altitude Acclimatization Tracking
Expected SpO2 at Altitude:
| Altitude | Approximate SpO2 |
| Sea level | 95-100% |
| 5,000 ft | 94-98% |
| 8,000 ft | 92-96% |
| 10,000 ft | 90-94% |
| 12,000 ft | 85-92% |
| 14,000 ft | 80-90% |
| 18,000 ft | 70-85% |
Acclimatization Progress:
Day 1 at Altitude:
- SpO2 drops significantly (e.g., from 98% to 88% at 12,000 ft)
Day 3-5:
- SpO2 improves 2-4% as body adapts (increased breathing, red blood cell changes)
Day 7-14:
- Further gradual improvement
- Stabilizes at new altitude-appropriate baseline
Poor Acclimatization:
If SpO2 remains very low (<75-80% at 12,000 ft) or fails to improve over days, descent is necessary.
Overnight Monitoring:
SpO2 should recover during sleep; failure to do so indicates inadequate acclimatization.
Correlating SpO2 with Other Metrics
SpO2 + Heart Rate:
Normal Relationship:
- Low SpO2 → sympathetic activation → increased heart rate (body compensates)
- During sleep apnea: HR drops during apnea → spikes upon arousal
Abnormal Pattern:
- Low SpO2 with low HR: Possible central sleep apnea, severe bradycardia
- Low SpO2 with very high HR: Possible severe hypoxemia, pulmonary embolism (emergency)
SpO2 + HRV:
Relationship:
- Adequate oxygenation supports parasympathetic activity (high HRV)
- Chronic hypoxemia → sympathetic dominance (low HRV)
Monitoring:
Improving SpO2 (through treatment of sleep apnea, COPD management, etc.) should correlate with improving HRV over weeks.
SpO2 + Temperature:
Illness Detection:
- Elevated temperature + declining SpO2 = likely respiratory infection
- Enables early detection before severe symptoms
SpO2 + Glucose (Diabetics):
Relationship:
- Hypoglycemia → altered mental status → sometimes slight SpO2 decrease
- Poor glucose control → vascular damage → reduced tissue oxygenation over time
Monitoring:
Combining CGM glucose data with SpO2 provides comprehensive metabolic-cardiovascular picture.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Emergency (Call 911 or Emergency Services):
✅ SpO2 <85% sustained
✅ SpO2 drop with severe symptoms (chest pain, confusion, inability to speak, severe shortness of breath)
✅ Rapid SpO2 decline (95% to <90% within hours)
Urgent (Same-Day Physician Contact):
✅ SpO2 <90% sustained for >10-15 minutes
✅ SpO2 88-92% with moderate symptoms (breathlessness, dizziness)
✅ New oxygen requirement (never needed supplemental oxygen before but now SpO2 low)
Schedule Appointment (Non-Urgent):
✅ SpO2 trending downward over days-weeks
✅ Exertional hypoxemia (low SpO2 only during activity)
✅ High sleep apnea screening score (ODI >15)
✅ Persistent borderline SpO2 (92-94% when normally higher)
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How accurate are smart ring SpO2 monitors compared to fingertip pulse oximeters?
A: Medical-grade smart rings using transmission pulse oximetry achieve accuracy comparable to clinical fingertip devices (±2-3%), while consumer-grade rings vary widely (±3-10%).
Detailed Comparison:
Medical Fingertip Pulse Oximeter (Gold Standard Wearable):
- Accuracy: ±2% across 70-100% SpO2 range
- Method: Transmission (light through fingertip)
- FDA-cleared as medical device
Medical-Grade Smart Ring (Transmission Technology):
- Accuracy: ±2-3% across 70-100% SpO2 range (when clinically validated)
- Method: Transmission (light through finger)
- FDA/CE medical device certification
Consumer Smart Ring (Variable Quality):
- Accuracy: ±3-4% (high-quality) to ±5-10% (low-quality)
- Method: Often reflectance or lower-quality transmission
- No medical device certification
Key Factors for Ring Accuracy:
Technology Type:
- Transmission method: More accurate (stronger signal, less interference)
- Reflectance method: Less accurate (weaker signal, more artifacts)
Clinical Validation:
- Tested against arterial blood gas? (gold standard)
- Published peer-reviewed studies?
- FDA/CE medical device clearance?
Sensor Quality:
- LED wavelength precision (660nm red, 940nm infrared)
- Photodetector sensitivity
- Signal processing algorithms
When Ring Accuracy Matches Fingertip:
✅ Medical-grade transmission ring
✅ Proper sizing (snug fit, good skin contact)
✅ Minimal motion (during sleep especially)
✅ Warm fingers (adequate blood flow)
✅ No nail polish on sensor finger
When Ring May Be Less Accurate:
❌ Consumer-grade device without validation
❌ Poor fit (too loose or too tight)
❌ During intense activity (motion artifacts)
❌ Very cold fingers (reduced blood flow)
Clinical Perspective:
Cardiologists and Pulmonologists:
Increasingly accept medical-grade smart ring data for:
- Sleep apnea screening
- COPD/heart failure trend monitoring
- Supplementary data between appointments
Not Accepted:
Ring data alone cannot diagnose conditions—confirms screening findings with formal testing or clinical correlation.
Q: Can I use a smart ring for sleep apnea diagnosis?
A: Smart rings provide screening and risk assessment for sleep apnea but cannot provide formal diagnosis. Diagnosis requires polysomnography (sleep study) or home sleep apnea test (HSAT).
What Smart Rings Can Do:
Screening:
- Identify high probability of OSA based on oxygen desaturations
- Calculate ODI (correlates with AHI from sleep study)
- Stratify risk (low/moderate/high)
Benefits of Ring Screening:
✅ Identifies who should pursue formal testing
✅ Avoids unnecessary sleep studies for low-risk individuals
✅ Convenient home monitoring over multiple nights
✅ Cost-effective first step
What Smart Rings Cannot Do:
❌ Definitive Diagnosis:
Only polysomnography or FDA-cleared home sleep apnea tests (HSAT) can diagnose OSA.
❌ AHI Calculation:
Rings estimate ODI (oxygen desaturations); AHI requires measuring actual breathing (apneas and hypopneas) via airflow sensors and respiratory effort belts.
❌ Sleep Apnea Type:
Cannot distinguish obstructive vs. central vs. mixed sleep apnea (requires respiratory effort monitoring).
❌ Treatment Prescription:
CPAP pressure settings, oral appliance fitting, or surgical decisions require formal diagnosis.
Appropriate Use Pathway:
Step 1: Smart Ring Screening
Wear ring for 3-7 nights → ODI calculated
Step 2: Risk Assessment
- Low ODI (<5): Reassurance, periodic re-screening
- Moderate ODI (5-15): Lifestyle modifications, discuss with physician
- High ODI (>15): Formal sleep study strongly recommended
Step 3: Formal Diagnosis
- Home sleep apnea test (HSAT): Portable device measuring breathing, oxygen, heart rate, position
- In-lab polysomnography: Comprehensive sleep study with brain waves, breathing, oxygen, heart, leg movements
Step 4: Treatment
- CPAP therapy, oral appliance, positional therapy, weight loss, or surgery based on diagnosis and severity
Step 5: Smart Ring Treatment Monitoring
- Track ODI improvement on therapy
- Detect non-adherence or equipment problems
- Long-term monitoring
Clinical Validation:
Studies Show:
Ring-based ODI correlates 0.85-0.92 with polysomnography AHI (strong correlation).
Sensitivity/Specificity:
High-quality rings detect moderate-severe OSA (AHI >15) with:
- Sensitivity: 85-92% (correctly identifies OSA)
- Specificity: 80-88% (correctly identifies no OSA)
Conclusion:
Excellent screening tool but formal diagnosis still required for treatment.
Q: What SpO2 level is dangerous?
A: SpO2 levels and urgency of medical attention depend on context, but general guidelines:
Critical (Emergency - Call 911):
- SpO2 <85% sustained
- Any SpO2 with severe symptoms: Confusion, chest pain, inability to speak, severe breathlessness, bluish lips/fingernails
Urgent (Seek Medical Care Same Day):
- **SpO2 <90%** sustained >10-15 minutes
- SpO2 88-92% with moderate symptoms (breathlessness, dizziness, rapid heart rate)
Concerning (Contact Physician):
- SpO2 92-94% sustained when normally higher
- SpO2 <90% during sleep (multiple episodes)
- Exertional hypoxemia (SpO2 <90% during activity)
Monitoring (Track Trends):
- SpO2 94-95% when normally 97-99% (investigate cause if sustained)
Important Context:
Chronic Conditions:
Some patients with COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, or heart failure have lower baseline SpO2 (88-92% may be their stable state). Their physician sets individual target ranges.
High Altitude:
Lower SpO2 is normal at elevation (85-92% acceptable at 12,000+ feet if asymptomatic and acclimatizing).
Age:
Elderly individuals may have slightly lower baseline (93-97% normal for some older adults).
Symptoms Matter More Than Numbers:
Asymptomatic SpO2 90%:
Still concerning and warrants medical evaluation, but less urgent than:
Symptomatic SpO2 92%:
If patient feels severe breathlessness, chest pain, or confusion at 92%, this is emergent.
Why:
- SpO2 monitors have ±2-3% error
- Individual oxygen delivery varies
- Some people tolerate lower SpO2 better than others
- Symptoms indicate inadequate tissue oxygenation regardless of number
When in Doubt:
If SpO2 is lower than expected or you feel unwell, seek medical advice. Better to err on side of caution.
Q: Can nail polish affect smart ring SpO2 readings?
A: Yes. Dark nail polish can significantly interfere with pulse oximetry, potentially causing inaccurate readings or measurement failure.
Why Nail Polish Interferes:
Light Absorption:
Pulse oximetry uses red (660nm) and infrared (940nm) light. Nail polish, especially dark colors, absorbs these wavelengths, blocking light transmission.
Most Problematic Colors:
- Black: Blocks most light (severe interference)
- Blue/Green: Absorbs red light strongly
- Purple/Brown: Moderate interference
- Glitter/Metallic: Reflects and scatters light
Least Problematic:
- Clear/Nude: Minimal interference
- Light Pink: Slight absorption
- Red: Absorbs less red light than blue/green/black
Impact on Readings:
Possible Effects:
- Falsely low SpO2 readings
- "Unable to measure" errors
- Intermittent signal loss
- Increased measurement variability
Severity:
Depends on polish opacity, thickness, and specific color pigments.
Solutions:
Option 1: Remove Polish from Sensor Finger
- If ring is on, e.g., ring finger, remove polish from that finger only
- Other fingers can keep polish
Option 2: Wear Ring on Different Finger
- Switch to finger without polish
- Ensure proper ring sizing for new finger
Option 3: Use Clear/Nude Polish
- Minimal interference with light transmission
Option 4: Remove Polish During Sleep
- If daytime aesthetics important but overnight monitoring critical, remove polish nightly (impractical for most)
Acrylic/Gel Nails:
Thicker Layers:
Acrylics and gel nails are thicker than regular polish, creating even more interference, especially if dark colored.
Recommendation:
If using smart ring for medical monitoring (sleep apnea, COPD, etc.), avoid dark acrylics/gels on sensor finger.
Testing:
Verify Accuracy:
If wearing polish, compare ring reading to a medical fingertip pulse oximeter on unpolished finger. If readings differ by >2-3%, polish likely interfering.
Q: How does altitude affect SpO2 readings?
A: Altitude dramatically affects SpO2 due to reduced atmospheric oxygen availability. This is normal physiology, not device malfunction.
Atmospheric Physics:
Sea Level:
- Atmospheric pressure: ~760 mmHg
- Oxygen percentage: 21% (constant at all altitudes)
- But: Higher pressure forces more oxygen into bloodstream
High Altitude:
- Atmospheric pressure: Lower (e.g., ~450 mmHg at 14,000 ft)
- Oxygen percentage: Still 21%
- But: Lower pressure means less oxygen enters bloodstream → lower SpO2
Expected SpO2 at Altitude:
Sea Level:
95-100% normal
Denver, CO (5,280 ft):
92-98% normal
Moderate Altitude (8,000-10,000 ft):
88-95% normal (initially); improves to 90-96% after acclimatization
High Altitude (10,000-14,000 ft):
80-92% normal (initially); improves to 85-94% after acclimatization
Very High Altitude (14,000-18,000 ft):
70-88% normal even after acclimatization
Extreme Altitude (>18,000 ft):
<80% common; requires supplemental oxygen for most people
Acclimatization Process:
Immediate Response (Hours):
- Increased breathing rate (hyperventilation)
- Increased heart rate
- SpO2 slightly improves
Short-Term (Days):
- Kidneys adjust blood pH (compensates for hyperventilation)
- SpO2 improves 2-5%
Long-Term (Weeks-Months):
- Increased red blood cell production (more oxygen-carrying capacity)
- Improved oxygen extraction at tissue level
- SpO2 stabilizes at altitude-appropriate level
Individual Variation:
Good Acclimatizers:
- SpO2 improves more quickly
- Tolerate lower SpO2 with fewer symptoms
- Genetic factors play role (Tibetan/Andean populations adapted over generations)
Poor Acclimatizers:
- SpO2 remains very low
- Symptoms despite time at altitude
- May require descent or supplemental oxygen
Altitude Sickness:
Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS):
- Symptoms: Headache, nausea, fatigue, dizziness
- SpO2 alone doesn't predict AMS (some people symptomatic at 88%, others asymptomatic at 80%)
- But: Very low SpO2 (<75% at 10,000-12,000 ft) increases risk
High-Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE):
- Life-threatening fluid in lungs
- SpO2 drops significantly (often <70-75% at moderate altitude)
- Requires immediate descent and oxygen
Monitoring:
Smart ring tracking SpO2 overnight helps identify poor acclimatization (SpO2 should recover during sleep; failure suggests inadequate adaptation).
Return to Sea Level:
SpO2 Normalization:
Within hours to days after descending, SpO2 returns to sea level baseline (95-100%).
Deacclimatization:
Red blood cell count gradually normalizes over weeks.
Q: Can smart rings detect COVID-19 or other illnesses?
A: Smart rings cannot diagnose specific illnesses like COVID-19, but they can detect physiological changes that often precede symptomatic illness, providing early warning of potential infection.
What Smart Rings Can Detect:
Early Physiological Changes (1-3 Days Before Symptoms):
Resting Heart Rate Elevation:
- Increase of 5-15 BPM from baseline
- Indicates immune system activation, inflammatory response
HRV Decrease:
- Reduction of 15-40% from baseline
- Reflects sympathetic nervous system dominance (stress response to illness)
SpO2 Slight Decrease:
- Drop of 1-3% from baseline (early stages)
- More significant drops (>5%) indicate developing respiratory infection
Respiratory Rate Increase:
- Breathing rate increases 2-4 breaths/minute
- Compensates for reduced oxygen exchange or fever
Body Temperature Elevation:
- Subtle increase (0.3-0.5°C) often precedes symptomatic fever
- May detect fever before user feels unwell
Sleep Disruption:
- Reduced deep sleep, increased awakenings
- Body prioritizes immune response over restorative sleep
COVID-19 Specific Research:
Studies During Pandemic:
Early Detection:
Wearable data predicted COVID-19 infection 1-3 days before symptom onset with 70-80% accuracy by combining:
- Elevated resting heart rate
- Decreased HRV
- Increased respiratory rate
- Body temperature elevation
- Sleep disturbances
Silent Hypoxemia Detection:
Many COVID-19 patients had dangerously low SpO2 without breathlessness ("happy hypoxemia").
Smart Ring Value:
- Detected SpO2 <92-94% prompting medical evaluation
- Enabled early hospitalization decisions
- Reduced sudden decompensation risk
Recovery Monitoring:
- Tracked return of physiological parameters to baseline
- Identified long COVID patients with persistent abnormalities
What Smart Rings Cannot Do:
❌ Identify Specific Pathogen:
Cannot distinguish COVID-19 from flu, RSV, bacterial infection, etc.
❌ Definitive Diagnosis:
Requires testing (PCR, antigen, etc.)
❌ Treatment Decisions:
Clinical evaluation needed for appropriate therapy
Appropriate Use:
Personal Health Surveillance:
- Notice unusual physiological changes
- Prompt earlier testing when changes detected
- Self-isolate proactively if multiple parameters abnormal
Earlier Medical Contact:
- Share wearable data showing physiological changes with physician
- Enables earlier evaluation and testing
- May prevent delayed diagnosis
Recovery Verification:
- Track normalization of HR, HRV, SpO2, sleep
- Guides return to activities
- Identifies prolonged recovery requiring medical attention
Evidence Base:
Peer-Reviewed Studies:
Multiple publications during COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated wearables detect physiological changes preceding symptomatic illness across various infections, not just COVID-19.
Mechanism:
Wearables detect nonspecific inflammatory and immune responses, which occur with most infections.
Conclusion
Continuous blood oxygen monitoring via smart rings represents a transformative advancement in accessible health technology. What once required hospital admission—continuous pulse oximetry surveillance—now fits comfortably on your finger, providing medical-grade data 24/7 without disrupting daily life.
Key Takeaways:
✅ Transmission pulse oximetry in rings achieves medical-grade accuracy: Comparable to clinical fingertip devices when properly validated
✅ Sleep apnea screening is the killer application: Rings excel at overnight monitoring, identifying millions of undiagnosed OSA cases
✅ Chronic disease management is transformed: COPD, heart failure, and other conditions benefit from continuous SpO2 surveillance enabling early intervention
✅ Altitude and athletic applications abound: Mountaineers, endurance athletes, and travelers gain objective acclimatization data
✅ Early illness detection works: SpO2 changes often precede symptomatic respiratory infections by 1-3 days
✅ Finger placement matters: Rings outperform wrist devices for SpO2 due to stronger signal, less motion, and transmission technology capability
✅ Medical-grade certification is essential for medical use: FDA/CE clearance confirms validation and accuracy for clinical decision-making
✅ Multi-parameter integration maximizes value: Combining SpO2 with heart rate, HRV, temperature, and sleep provides holistic health picture
The democratization of continuous SpO2 monitoring empowers individuals to take proactive control of respiratory and cardiovascular health. From detecting silent hypoxemia during pandemics to screening for sleep apnea, from managing chronic lung disease to optimizing altitude training, smart rings bring hospital-grade oxygen monitoring to everyday life.
Choose your device based on clinical validation, regulatory certification, and feature alignment with your health goals. Establish personal baselines, understand normal variation, and respond appropriately to concerning patterns. Share data with healthcare providers when indicated, recognizing that wearables are screening and monitoring tools that complement—not replace—clinical care.
Your oxygen saturation tells a continuous story about respiratory function, cardiovascular health, sleep quality, and overall wellness. Smart ring technology ensures you never miss a chapter.
Additional Resources:
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Sleep apnea information and treatment guidelines (aasm.org)
- COPD Foundation: Chronic respiratory disease management resources (copdfoundation.org)
- American Lung Association: Respiratory health education (lung.org)
- Wilderness Medical Society: Altitude illness prevention and treatment guidelines (wms.org)
- FDA Medical Device Database: Verify device regulatory status (accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/devicesatfda)
Medical Disclaimer:
This guide provides educational information about blood oxygen monitoring technology. It is not medical advice. Smart rings are health monitoring tools; only medical-grade devices with regulatory approval should be used for clinical decision-making. Consumer devices are screening tools, not diagnostic devices. Always consult qualified healthcare providers for diagnosis, treatment, and medical decisions. If you experience symptoms of low oxygen (confusion, severe breathlessness, chest pain, bluish discoloration), seek immediate emergency medical attention—do not rely solely on wearable device data.
This guide was last updated in February 9, 2026. SpO2 monitoring technology and clinical validation standards evolve rapidly—verify current device capabilities, accuracy data, and regulatory status before purchase.
Related Articles:
How Do Smart Rings Revolutionize Sleep Monitoring And OSA Risk Assessment?
Smart Band vs Smart Bracelet vs Fitness Tracker: Key Differences Explained
White Label vs OEM Wearables: Which Is the Right Choice for Your Brand?
About the Author

Kyler is a senior content marketing specialist at J-Style(Jointcorp|Joint Chinese Ltd | Youhong Medical), a leading smart ring, smart band, and smart watch manufacturer and supplier in China. With 8 years of experience in the wearable tech industry, he creates professional content for global B2B buyers seeking reliable factory, wholesale, OEM/ODM, and SDK/API solutions. At J-Style, Kyler focuses on helping partners understand the value of high-quality Chinese smart wearables and how J-Style’s innovative manufacturing capabilities support scalable business growth.






